Virtual High-Throughput Screening for Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors
- PMID: 28299742
- PMCID: PMC6485679
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6863-3_14
Virtual High-Throughput Screening for Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors
Abstract
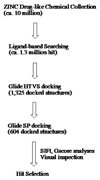
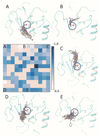
Structure-based virtual screening (SBVS) is a common method for the fast identification of hit structures at the beginning of a medicinal chemistry program in drug discovery. The SBVS, described in this manuscript, is focused on finding small molecule hits that can be further utilized as a starting point for the development of inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP-13) via structure-based molecular design. We intended to identify a set of structurally diverse hits, which occupy all subsites (S1'-S3', S2, and S3) centering the zinc containing binding site of MMP-13, by the virtual screening of a chemical library comprising more than ten million commercially available compounds. In total, 23 compounds were found as potential MMP-13 inhibitors using Glide docking followed by the analysis of the structural interaction fingerprints (SIFt) of the docked structures.
Keywords: Docking; Matrix metalloproteinase; Structural interaction fingerprints; Structure-based virtual screening; Zn-chelating inhibitor.
Figures

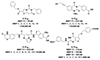
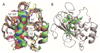
References
-
- Ripphausen P, et al. Quo Vadis, Virtual Screening? A Comprehensive Survey of Prospective Applications. J Med Chem. 2010;53(24):8461–8467. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh S, et al. Structure-based virtual screening of chemical libraries for drug discovery. Curr Opin Chem Bio. 2006;10(3):194–202. - PubMed
-
- Takaishi H, et al. Joint diseases and matrix metalloproteinases: A role for MMP-13. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2008;9(1):47–54. - PubMed
-
- Zigrino P, et al. Stromal Expression of MMP-13 is Required for Melanoma Invasion and Metastasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129(11):2686–2693. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

