Iridium-catalysed regioselective borylation of carboranes via direct B-H activation
- PMID: 28300061
- PMCID: PMC5357313
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14827
Iridium-catalysed regioselective borylation of carboranes via direct B-H activation
Abstract
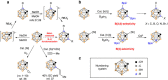
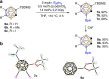
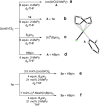
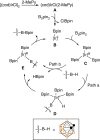
Carboranes are carbon-boron molecular clusters, which can be viewed as three-dimensional analogues to benzene. They are finding many applications in medicine, materials and organometallic chemistry. On the other hand, their exceptional thermal and chemical stabilities, as well as 3D structures, make them very difficult to be functionalized, in particular the regioselective functionalization of BH vertex among ten similar B-H bonds. Here we report a very efficient iridium-catalysed borylation of cage B(3,6)-H bonds of o-carboranes with excellent yields and regioselectivity using bis(pinacolato)diboron (B2pin2) as a reagent. Selective cage B(4)-H borylation has also been achieved by introducing a bulky TBDMS (tert-butyldimethylsilyl) group to one cage carbon vertex. The resultant 3,6-(Bpin)2-o-carboranes are useful synthons for the synthesis of a wide variety of B(3,6)-difunctionalized o-carboranes bearing cage B-X (X=O, N, C, I and Br) bonds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Strategy for Selective Catalytic B-H Functionalization of o-Carboranes.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Nov 2;54(21):4065-4079. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00460. Epub 2021 Oct 24. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34693715
-
Controlled functionalization of o-carborane via transition metal catalyzed B-H activation.Chem Soc Rev. 2019 Jul 1;48(13):3660-3673. doi: 10.1039/c9cs00169g. Chem Soc Rev. 2019. PMID: 31090766 Review.
-
Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Selective Cage B-H Functionalization of o-Carboranes.Chemistry. 2018 Feb 26;24(12):2795-2805. doi: 10.1002/chem.201704937. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Chemistry. 2018. PMID: 29148596
-
Transition Metal Catalyzed, Regioselective B(4)-Halogenation and B(4,5)-Diiodination of Cage B-H Bonds in o-Carboranes.Chemistry. 2017 Oct 20;23(59):14866-14871. doi: 10.1002/chem.201703006. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 28758706
-
Transition metal-carboryne complexes: synthesis, bonding, and reactivity.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Apr 19;44(4):299-309. doi: 10.1021/ar100156f. Epub 2011 Mar 11. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21395260 Review.
Cited by
-
Expanding the Scope of Palladium-Catalyzed B - N Cross-Coupling Chemistry in Carboranes.Organometallics. 2020 Dec 14;39(23):4380-4386. doi: 10.1021/acs.organomet.0c00576. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Organometallics. 2020. PMID: 34012188 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodium catalyzed cascade cyclization featuring B-H and C-H activation: one-step construction of carborane-fused N-polyheterocycles.Chem Sci. 2018 Jun 29;9(30):6390-6394. doi: 10.1039/c8sc01568f. eCollection 2018 Aug 14. Chem Sci. 2018. PMID: 30310567 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid reversible borane to boryl hydride exchange by metal shuttling on the carborane cluster surface.Chem Sci. 2017 Aug 1;8(8):5399-5407. doi: 10.1039/c7sc01846k. Epub 2017 May 25. Chem Sci. 2017. PMID: 28970919 Free PMC article.
-
Improved synthesis of icosahedral carboranes containing exopolyhedral B-C and C-C bonds.Tetrahedron. 2019 Jan 11;75(2):187-191. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2018.11.040. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Tetrahedron. 2019. PMID: 31303685 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Carborane-Based Crystalline Porous Materials.Molecules. 2024 Aug 19;29(16):3916. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163916. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grimes R. M. Carboranes 2nd edn Academic Press (2011).
-
- Hosmane N. S. Boron Science: New Technologies and Applications CRC (2012).
-
- Hawthorne M. F. The role of chemistry in the development of boron neutron capture therapy of cancer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 32, 950–984 (1993).
-
- Soloway A. H. et al.. The chemistry of neutron capture therapy. Chem. Rev. 98, 1515–1562 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Armstrong A. F. & Valliant J. F. The bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry of carboranes: from new drug discovery to molecular imaging and therapy. Dalton Trans. 4240–4251 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

