Actin-binding protein coronin 1A controls osteoclastic bone resorption by regulating lysosomal secretion of cathepsin K
- PMID: 28300073
- PMCID: PMC5353622
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41710
Actin-binding protein coronin 1A controls osteoclastic bone resorption by regulating lysosomal secretion of cathepsin K
Abstract
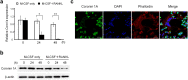
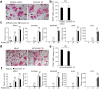
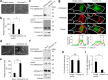
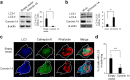
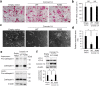
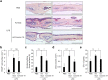
Osteoclasts degrade bone matrix proteins via the secretion of lysosomal enzymes. However, the precise mechanisms by which lysosomal components are transported and fused to the bone-apposed plasma membrane, termed ruffled border membrane, remain elusive. Here, we identified coronin 1A as a negative regulator of exocytotic release of cathepsin K, one of the most important bone-degrading enzymes in osteoclasts. The modulation of coronin 1A expression did not alter osteoclast differentiation and extracellular acidification, but strongly affected the secretion of cathepsin K and osteoclast bone-resorption activity, suggesting the coronin 1A-mediated regulation of lysosomal trafficking and protease exocytosis. Further analyses suggested that coronin 1A prevented the lipidation-mediated sorting of the autophagy-related protein LC3 to the ruffled border and attenuated lysosome-plasma membrane fusion. In this process, the interactions between coronin 1A and actin were crucial. Collectively, our findings indicate that coronin 1A is a pivotal component that regulates lysosomal fusion and the secretion pathway in osteoclast-lineage cells and may provide a novel therapeutic target for bone diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
S.O., T.F. and M. Asagiri were partly employed by the Coordination Fund from the Japan Science and Technology Agency and Astellas Pharma Inc.; and T.F. and M. Asagiri received research grants from this fund. K.I. is employed by the Coordination Fund from Kyoto University and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; and receive research grants from this fund. The authors have no additional conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Suda T. et al.. Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev 20, 345–357 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Boyle W. J., Simonet W. S. & Lacey D. L. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 423, 337–342 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Asagiri M. & Takayanagi H. The molecular understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone 40, 251–264 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

