A comparison between hydrogel spacer and endorectal balloon: An analysis of intrafraction prostate motion during proton therapy
- PMID: 28300377
- PMCID: PMC5689955
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12051
A comparison between hydrogel spacer and endorectal balloon: An analysis of intrafraction prostate motion during proton therapy
Abstract
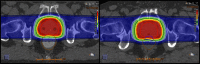
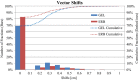
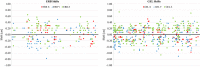
The purpose of this study was to evaluate intrafraction prostate motion in patients treated with proton therapy and an endorectal balloon or a hydrogel spacer using orthogonal x-rays acquired before and after each treatment field. This study evaluated 10 patients (662 fields throughout treatment) treated daily with an endorectal balloon (ERB) and 16 patients (840 fields throughout treatment) treated with a hydrogel spacer (GEL) without an ERB. Patient shifts were recorded before and after each treatment field, correlated with a treatment time, using x-ray imaging and implanted fiducial alignment. For each shift, recorded in X, Y, and Z, a 3D vector was calculated to determine the positional change. There was a statistically significant difference in the mean vector shift between ERB (0.06 cm) and GEL (0.09 cm), (P < 0.001). The mean includes a large number of zero shifts, but the smallest non-zero shift recorded was 0.2 cm. The largest shifts were, on average, in the Z direction (anterior to posterior). The average Z shift was +0.02 cm for both ERB and GEL. There was no statistical difference between ERB and GEL for shifts greater than 0.3 cm (P = 0.13) or greater than 0.5 cm (P = 0.36). For treatment times between 5 and 9 min, a majority of shifts were less than 0.2 cm, 85.9% for ERB and 73.2% for GEL. There was a significant positive correlation between the vector shifts and field time for both ERB (r = 0.2, P < 0.001) and GEL (r = 0.07, P < 0.04). We have shown that prostate motion is clinically comparable between an ERB and a hydrogel spacer, and the time dependencies are similar. A large majority of shifts for both ERB and hydrogel are well within a typical robust planning margin. For GEL patients, we chose to maintain slightly larger planning margins than for ERB due to already improved rectal sparing with GEL.
Keywords: SpaceOAR; endorectal balloon; hydrogel; motion; prostate; proton therapy.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A study to quantify the effectiveness of daily endorectal balloon for prostate intrafraction motion management.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Jul 1;83(3):1055-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.07.038. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22115790
-
An endorectal balloon reduces intrafraction prostate motion during radiotherapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Jun 1;83(2):661-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.07.028. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22099035
-
Prostate and patient intrafraction motion: impact on treatment time-dependent planning margins for patients with endorectal balloon.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013 Jul 15;86(4):755-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.02.035. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013. PMID: 23582854
-
Effectiveness of rectal displacement devices in managing prostate motion: a systematic review.Strahlenther Onkol. 2021 Feb;197(2):97-115. doi: 10.1007/s00066-020-01633-9. Epub 2020 May 22. Strahlenther Onkol. 2021. PMID: 32444903
-
Absorbable Hydrogel Spacer Use in Prostate Radiotherapy: A Comprehensive Review of Phase 3 Clinical Trial Published Data.Urology. 2018 May;115:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2017.11.016. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Urology. 2018. PMID: 29174940 Review.
Cited by
-
Preliminary analysis of prostate positional displacement using hydrogel spacer during the course of proton therapy for prostate cancer.J Radiat Res. 2021 Mar 10;62(2):294-299. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rraa115. J Radiat Res. 2021. PMID: 33341901 Free PMC article.
-
Intrafraction Prostate Motion Management for Ultra-Hypofractionated Radiotherapy of Prostate Cancer.Curr Oncol. 2022 Aug 31;29(9):6314-6324. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29090496. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36135065 Free PMC article.
-
A novel model to correlate hydrogel spacer placement, perirectal space creation, and rectum dosimetry in prostate stereotactic body radiotherapy.Radiat Oncol. 2018 Oct 1;13(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-1135-6. Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30285812 Free PMC article.
-
Injection of hydrogel spacer increased maximal intrafractional prostate motion in anterior and superior directions during volumetric modulated arc therapy-stereotactic body radiation therapy for prostate cancer.Radiat Oncol. 2022 Feb 23;17(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13014-022-02008-3. Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35197092 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering: Addressing Key Design Needs Toward Clinical Translation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 May 5;10:849831. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.849831. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35600900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Both S, Wang KK‐H, Plastaras JP, et al. Real‐time study of prostate intrafraction motion during external beam radiotherapy with daily endorectal balloon. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81:1302–1309. - PubMed
-
- Smeenk RJ, Louwe RJW, Langen KM, et al. An endorectal balloon reduces intrafraction prostate motion during radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;832:661–669. - PubMed
-
- Gysen K, Kneebone A, Alfieri F, Guo L, Eade T. Feasibility of and rectal dosimetry improvement with the use of SpaceOAR® hydrogel for dose‐escalated prostate cancer radiotherapy. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2014;58:511–516. - PubMed
-
- Madsen BL, Hsi RA, Pham HT, et al. Stereotactic hypofractionated accurate radiotherapy of the prostate (SHARP), 33.5 Gy in five fractions for localized disease: First clinical trial results. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67:1099–1105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

