The connective tissue phenotype of glaucomatous cupping in the monkey eye - Clinical and research implications
- PMID: 28300644
- PMCID: PMC5603293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2017.03.001
The connective tissue phenotype of glaucomatous cupping in the monkey eye - Clinical and research implications
Abstract
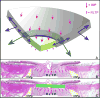
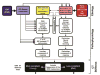
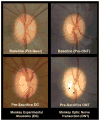
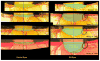
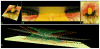
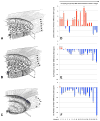
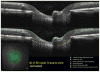
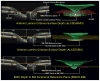
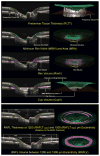
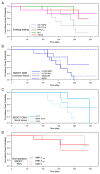
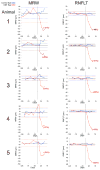
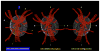
In a series of previous publications we have proposed a framework for conceptualizing the optic nerve head (ONH) as a biomechanical structure. That framework proposes important roles for intraocular pressure (IOP), IOP-related stress and strain, cerebrospinal fluid pressure (CSFp), systemic and ocular determinants of blood flow, inflammation, auto-immunity, genetics, and other non-IOP related risk factors in the physiology of ONH aging and the pathophysiology of glaucomatous damage to the ONH. The present report summarizes 20 years of technique development and study results pertinent to the characterization of ONH connective tissue deformation and remodeling in the unilateral monkey experimental glaucoma (EG) model. In it we propose that the defining pathophysiology of a glaucomatous optic neuropathy involves deformation, remodeling, and mechanical failure of the ONH connective tissues. We view this as an active process, driven by astrocyte, microglial, fibroblast and oligodendrocyte mechanobiology. These cells, and the connective tissue phenomena they propagate, have primary and secondary effects on retinal ganglion cell (RGC) axon, laminar beam and retrolaminar capillary homeostasis that may initially be "protective" but eventually lead to RGC axonal injury, repair and/or cell death. The primary goal of this report is to summarize our 3D histomorphometric and optical coherence tomography (OCT)-based evidence for the early onset and progression of ONH connective tissue deformation and remodeling in monkey EG. A second goal is to explain the importance of including ONH connective tissue processes in characterizing the phenotype of a glaucomatous optic neuropathy in all species. A third goal is to summarize our current efforts to move from ONH morphology to the cell biology of connective tissue remodeling and axonal insult early in the disease. A final goal is to facilitate the translation of our findings and ideas into neuroprotective interventions that target these ONH phenomena for therapeutic effect.
Keywords: Astrocyte; Glaucoma; Lamina cribrosa; Monkey; Optic nerve head.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

























References
-
- Alm A, Bill A. The oxygen supply to the retina. II. Effects of high intraocular pressure and of increased arterial carbon dioxide tension on uveal and retinal blood flow in cats. A study with radioactively labelled microspheres including flow determinations in brain and some other tissues. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972;84:306–319. - PubMed
-
- Alm A, Bill A. Ocular and optic nerve blood flow at normal and increased intraocular pressures in monkeys (Macaca irus): a study with radioactively labelled microspheres including flow determinations in brain and some other tissues. Exp Eye Res. 1973;15:15–29. - PubMed
-
- Anderson DR, Hendrickson A. Effect of intraocular pressure on rapid axoplasmic transport in monkey optic nerve. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974;13:771–783. - PubMed
-
- Anderson DR, Hoyt WF. Ultrastructure of intraorbital portion of human and monkey optic nerve. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969;82:506–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

