Scleromyxedema: clinical diagnosis and autopsy findings
- PMID: 28300892
- PMCID: PMC5324991
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164527
Scleromyxedema: clinical diagnosis and autopsy findings
Abstract
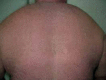
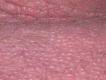
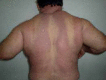
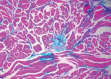
Scleromyxedema is a rare chronic cutaneous mucinosis of unknown etiology. It is characterized by papular eruption and scleroderma with microscopic evidence of mucin deposition, fibroblast proliferation, and fibrosis. Most patients with scleromyxedema have monoclonal gammopathy and systemic manifestations resulting in significant morbidity and mortality. Several types of treatment have been reported with partial or inconsistent responses. Despite showing unpredictable evolution, systemic consequences of scleromyxedema and treatment side effects may result in death. We describe a rare case of a patient with scleromyxedema without paraproteinemia with systemic involvement that evolved to death despite treatment with cyclophosphamide.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None
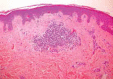
Figures
References
-
- Heymann WR. Scleromyxedema. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:890–891. - PubMed
-
- Guarenti I, Sebastiani V, Pinto G, de Souza PR, de Almeida H., Jr Successful treatment of scleromyxedema with oral thalidomide. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:631–632. - PubMed
-
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, Fausti V, Cozzani E, Cribier B, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66–72. - PubMed
-
- Rey JB, Luria RB. Treatment of scleromyxedema and the dermatoneuro syndrome with intravenous immunoglobulin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:1037–1041. - PubMed
-
- Fleming KE, Virmani D, Sutton E, Langley R, Corbin J, Pasternak S, et al. Scleromyxedema and the dermato-neuro syndrome: case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:508–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
