Benchmarking of participant-level confound regression strategies for the control of motion artifact in studies of functional connectivity
- PMID: 28302591
- PMCID: PMC5483393
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.03.020
Benchmarking of participant-level confound regression strategies for the control of motion artifact in studies of functional connectivity
Abstract
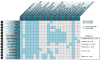
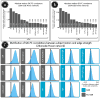
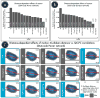
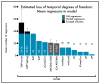
Since initial reports regarding the impact of motion artifact on measures of functional connectivity, there has been a proliferation of participant-level confound regression methods to limit its impact. However, many of the most commonly used techniques have not been systematically evaluated using a broad range of outcome measures. Here, we provide a systematic evaluation of 14 participant-level confound regression methods in 393 youths. Specifically, we compare methods according to four benchmarks, including the residual relationship between motion and connectivity, distance-dependent effects of motion on connectivity, network identifiability, and additional degrees of freedom lost in confound regression. Our results delineate two clear trade-offs among methods. First, methods that include global signal regression minimize the relationship between connectivity and motion, but result in distance-dependent artifact. In contrast, censoring methods mitigate both motion artifact and distance-dependence, but use additional degrees of freedom. Importantly, less effective de-noising methods are also unable to identify modular network structure in the connectome. Taken together, these results emphasize the heterogeneous efficacy of existing methods, and suggest that different confound regression strategies may be appropriate in the context of specific scientific goals.
Keywords: Artifact; Confound; Functional connectivity; Motion; Noise; fMRI.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P50 MH096891/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB022573/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089973/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH107235/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC009209/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH106799/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101111/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089924/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH102609/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD086888/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS085211/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH107703/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089983/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

