Expansions of Cytotoxic CD4+CD28- T Cells Drive Excess Cardiovascular Mortality in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Other Chronic Inflammatory Conditions and Are Triggered by CMV Infection
- PMID: 28303136
- PMCID: PMC5332470
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00195
Expansions of Cytotoxic CD4+CD28- T Cells Drive Excess Cardiovascular Mortality in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Other Chronic Inflammatory Conditions and Are Triggered by CMV Infection
Abstract
A large proportion of cardiovascular (CV) pathology results from immune-mediated damage, including systemic inflammation and cellular proliferation, which cause a narrowing of the blood vessels. Expansions of cytotoxic CD4+ T cells characterized by loss of CD28 ("CD4+CD28- T cells" or "CD4+CD28null cells") are closely associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD), in particular coronary artery damage. Direct involvement of these cells in damaging the vasculature has been demonstrated repeatedly. Moreover, CD4+CD28- T cells are significantly increased in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other autoimmune conditions. It is striking that expansions of this subset beyond 1-2% occur exclusively in CMV-infected people. CMV infection itself is known to increase the severity of autoimmune diseases, in particular RA and has also been linked to increased vascular pathology. A review of the recent literature on immunological changes in CVD, RA, and CMV infection provides strong evidence that expansions of cytotoxic CD4+CD28- T cells in RA and other chronic inflammatory conditions are limited to CMV-infected patients and driven by CMV infection. They are likely to be responsible for the excess CV mortality observed in these situations. The CD4+CD28- phenotype convincingly links CMV infection to CV mortality based on a direct cellular-pathological mechanism rather than epidemiological association.
Keywords: CD4 T cells; autoimmune diseases; cardiovascular diseases; chronic inflammatory disease; cytotoxic T cells.
Figures
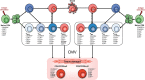
References
-
- Vallejo AN, Brandes JC, Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Modulation of CD28 expression: distinct regulatory pathways during activation and replicative senescence. J Immunol (1999) 162(11):6572–9. - PubMed
-
- Liuzzo G, Kopecky SL, Frye RL, O’Fallon WM, Maseri A, Goronzy JJ, et al. Perturbation of the T-cell repertoire in patients with unstable angina. Circulation (1999) 100(21):2135–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

