Bone Alkaline Phosphatase and Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase: Potential Co-regulators of Bone Mineralization
- PMID: 28303318
- PMCID: PMC5486932
- DOI: 10.1007/s00223-017-0259-2
Bone Alkaline Phosphatase and Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase: Potential Co-regulators of Bone Mineralization
Abstract
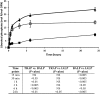
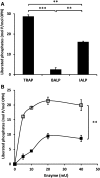
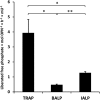
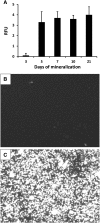
Phosphorylated osteopontin (OPN) inhibits hydroxyapatite crystal formation and growth, and bone alkaline phosphatase (BALP) promotes extracellular mineralization via the release of inorganic phosphate from the mineralization inhibitor inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), produced by osteoclasts, osteoblasts, and osteocytes, exhibits potent phosphatase activity towards OPN; however, its potential capacity as a regulator of mineralization has not previously been addressed. We compared the efficiency of BALP and TRAP towards the endogenous substrates for BALP, i.e., PPi and pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP), and their impact on mineralization in vitro via dephosphorylation of bovine milk OPN. TRAP showed higher phosphatase activity towards phosphorylated OPN and PPi compared to BALP, whereas the activity of TRAP and BALP towards PLP was comparable. Bovine milk OPN could be completely dephosphorylated by TRAP, liberating all its 28 phosphates, whereas BALP dephosphorylated at most 10 phosphates. OPN, dephosphorylated by either BALP or TRAP, showed a partially or completely attenuated phosphorylation-dependent inhibitory capacity, respectively, compared to native OPN on the formation of mineralized nodules. Thus, there are phosphorylations in OPN important for inhibition of mineralization that are removed by TRAP but not by BALP. In conclusion, our data indicate that both BALP and TRAP can alleviate the inhibitory effect of OPN on mineralization, suggesting a potential role for TRAP in skeletal mineralization. Further studies are warranted to explore the possible physiological relevance of TRAP in bone mineralization.
Keywords: Bone; Dephosphorylation; Hydroxyapatite; Inorganic pyrophosphate; Mineralization; Osteopontin.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors Cecilia Halling Linder, Barbro Ek-Rylander, Michael Krumpel, Maria Norgård, Sonoko Narisawa, José Luis Millán, Göran Andersson, and Per Magnusson declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

