E6/E7-P53-POU2F1-CTHRC1 axis promotes cervical cancer metastasis and activates Wnt/PCP pathway
- PMID: 28303973
- PMCID: PMC5356195
- DOI: 10.1038/srep44744
E6/E7-P53-POU2F1-CTHRC1 axis promotes cervical cancer metastasis and activates Wnt/PCP pathway
Abstract
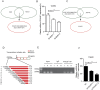
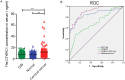
Cervical cancer is an infectious cancer and the most common gynecologic cancer worldwide. E6/E7, the early genes of the high-risk mucosal human papillomavirus type, play key roles in the carcinogenic process of cervical cancer. However, little was known about its roles in modulating tumor microenvironment, particular extracellular matrix (ECM). In this study, we found that E6/E7 could regulate multiple ECM proteins, especially collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 (CTHRC1). CTHRC1 is highly expressed in cervical cancer tissue and serum and closely correlated with clinicopathological parameters. CTHRC1 promotes cervical cancer cell migration and invasion in vitro and metastasis in vivo. E6/E7 regulates the expression of CTHRC1 in cervical cancer by E6/E7-p53-POU2F1 (POU class 2 homeobox 1) axis. Futhermore, CTHRC1 activates Wnt/PCP signaling pathway. Take together, E6/E7-p53-POU2F1-CTHRC1 axis promotes cervical cancer cell invasion and metastasis and may act as a potential therapeutic target for interventions against cervical cancer invasion and metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

