Facile synthesis of chlorin bioconjugates by a series of click reactions
- PMID: 28304032
- PMCID: PMC5463999
- DOI: 10.1039/c7cc01265a
Facile synthesis of chlorin bioconjugates by a series of click reactions
Abstract
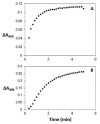
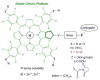
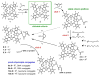
A multifunctional chlorin platform appended with four short polyethylene glycols and a carboxylate-linker allows rapid conjugation to biotargeting motifs such as proteins and oligonucleotides. The stability and photophysical properties of the chlorin enable development of diagnostics, imaging, molecular tracking, and theranostics.
Figures

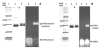
References
-
- Dąbrowski JM, Pucelik B, Regiel-Futyra A, Brindell M, Mazuryk O, Kyzioł A, Stochel G, Macyk W, Arnaut LG. Coord Chem Rev. 2016;325:67–101.
-
- Bonnett R, Charlesworth P, Djelal BD, Foley S, McGarvey DJ, Truscott TG. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 2. 1999:325–328.
-
- Detty MR, Gibson SL, Wagner SJ. J Med Chem. 2004;47:3897–3915. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

