Automatic ICD-10 coding algorithm using an improved longest common subsequence based on semantic similarity
- PMID: 28306739
- PMCID: PMC5356997
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173410
Automatic ICD-10 coding algorithm using an improved longest common subsequence based on semantic similarity
Abstract
ICD-10(International Classification of Diseases 10th revision) is a classification of a disease, symptom, procedure, or injury. Diseases are often described in patients' medical records with free texts, such as terms, phrases and paraphrases, which differ significantly from those used in ICD-10 classification. This paper presents an improved approach based on the Longest Common Subsequence (LCS) and semantic similarity for automatic Chinese diagnoses, mapping from the disease names given by clinician to the disease names in ICD-10. LCS refers to the longest string that is a subsequence of every member of a given set of strings. The proposed method of improved LCS in this paper can increase the accuracy of processing in Chinese disease mapping.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
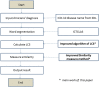

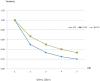



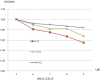


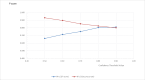
Similar articles
-
Longest common substring in Longest Common Subsequence's solution service: A novel hyper-heuristic.Comput Biol Chem. 2023 Aug;105:107882. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2023.107882. Epub 2023 May 19. Comput Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37244077
-
A hyper-heuristic for the Longest Common Subsequence problem.Comput Biol Chem. 2012 Feb;36:42-54. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2011.12.004. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Comput Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22286085
-
Analysis and safety engineering of fuzzy string matching algorithms.ISA Trans. 2021 Jul;113:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2020.10.014. Epub 2020 Oct 11. ISA Trans. 2021. PMID: 33092862
-
International classification of disease coding for obstructive lung disease: does it reflect appropriate clinical documentation?Chest. 2010 Jul;138(1):188-92. doi: 10.1378/chest.09-1342. Chest. 2010. PMID: 20605817 Review.
-
Classifying external causes of injury: history, current approaches, and future directions.Epidemiol Rev. 2012;34:4-16. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxr014. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Epidemiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22045696 Review.
Cited by
-
EHR problem list clustering for improved topic-space navigation.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019 Apr 4;19(Suppl 3):72. doi: 10.1186/s12911-019-0789-9. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019. PMID: 30943968 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging Shannon Entropy to Validate the Transition between ICD-10 and ICD-11.Entropy (Basel). 2018 Oct 8;20(10):769. doi: 10.3390/e20100769. Entropy (Basel). 2018. PMID: 33265857 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of different feature extraction methods for applicable automated ICD coding.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022 Jan 12;22(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12911-022-01753-5. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022. PMID: 35022039 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence Algorithm with ICD Coding Technology Guided by the Embedded Electronic Medical Record System in Medical Record Information Management.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Aug 30;2021:3293457. doi: 10.1155/2021/3293457. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. PMID: 34497706 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic ICD Code Assignment based on ICD's Hierarchy Structure for Chinese Electronic Medical Records.AMIA Jt Summits Transl Sci Proc. 2019 May 6;2019:417-424. eCollection 2019. AMIA Jt Summits Transl Sci Proc. 2019. PMID: 31258995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arifo˘glu D, Deniz O, Aleçakır K and Yöndem M. CodeMagic: Semi-Automatic Assignment of ICD-10-AM Codes to Patient Records. Information Sciences and Systems. 2014:259–268
-
- Boytcheva S. Automatic Matching of ICD-10 codes to Diagnoses in Discharge Letters. Proceedings of the Workshop on Biomedical Natural Language Processing. 2011;9:11–18
-
- Patrick J, Zhang Y, Wang Y. Developing feature types for classifying clinical notes. Proceedings of the Workshop on BioNLP 2007: Biological, Translational, and Clinical Language Processing; 2007.pp.191–192
-
- Zweigenbaum P, Lavergne T, Hybrid methods for ICD-10 coding of death certificates, Proceedings of the Seventh International Workshop on Health Text Mining and Information Analysis (LOUHI); 2016.pp.96–105
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

