Effect of Moderate-Intensity Exercise Training on Peak Oxygen Consumption in Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 28306757
- PMCID: PMC5469299
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2017.2503
Effect of Moderate-Intensity Exercise Training on Peak Oxygen Consumption in Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Erratum in
-
Missing Author Middle Initial.JAMA. 2017 May 23;317(20):2134. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.5228. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28535213 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Formulating exercise recommendations for patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is challenging because of concern about triggering ventricular arrhythmias and because a clinical benefit has not been previously established in this population.
Objective: To determine whether moderate-intensity exercise training improves exercise capacity in adults with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Design, setting, and participants: A randomized clinical trial involving 136 patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy was conducted between April 2010 and October 2015 at 2 academic medical centers in the United States (University of Michigan Health System and Stanford University Medical Center). Date of last follow-up was November 2016.
Interventions: Participants were randomly assigned to 16 weeks of moderate-intensity exercise training (n = 67) or usual activity (n = 69).
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome measure was change in peak oxygen consumption from baseline to 16 weeks.
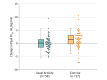
Results: Among the 136 randomized participants (mean age, 50.4 [SD, 13.3] years; 42% women), 113 (83%) completed the study. At 16 weeks, the change in mean peak oxygen consumption was +1.35 (95% CI, 0.50 to 2.21) mL/kg/min among participants in the exercise training group and +0.08 (95% CI, -0.62 to 0.79) mL/kg/min among participants in the usual-activity group (between-group difference, 1.27 [95% CI, 0.17 to 2.37]; P = .02). There were no occurrences of sustained ventricular arrhythmia, sudden cardiac arrest, appropriate defibrillator shock, or death in either group.
Conclusions and relevance: In this preliminary study involving patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, moderate-intensity exercise compared with usual activity resulted in a statistically significant but small increase in exercise capacity at 16 weeks. Further research is needed to understand the clinical importance of this finding in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, as well as the long-term safety of exercise at moderate and higher levels of intensity.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT01127061.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Exercise for Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy.JAMA. 2017 Aug 1;318(5):480-481. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.8193. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28763541 No abstract available.
References
-
- Semsarian C, Ingles J, Maron MS, Maron BJ. New perspectives on the prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(12):1249-1254. - PubMed
-
- Alcalai R, Seidman JG, Seidman CE. Genetic basis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: from bench to the clinics. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2008;19(1):104-110. - PubMed
-
- Braunwald E, Lambrew CT, Rockoff SD, Ross J Jr, Morrow AG. Idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, I: a description of the disease based upon an analysis of 64 patients. Circulation. 1964;30(suppl 4):3-119. - PubMed
-
- Maron BJ, Casey SA, Poliac LC, Gohman TE, Almquist AK, Aeppli DM. Clinical course of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a regional United States cohort. JAMA. 1999;281(7):650-655. - PubMed
-
- Gersh BJ, Maron BJ, Bonow RO, et al. ; American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines; American Association for Thoracic Surgery; American Society of Echocardiography; American Society of Nuclear Cardiology; Heart Failure Society of America; Heart Rhythm Society; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions; Society of Thoracic Surgeons . 2011 ACCF/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2011;124(24):2761-2796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

