Preclinical evaluation of the efficacy, pharmacokinetics and immunogenicity of JS-001, a programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) monoclonal antibody
- PMID: 28317872
- PMCID: PMC5457696
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2016.161
Preclinical evaluation of the efficacy, pharmacokinetics and immunogenicity of JS-001, a programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) monoclonal antibody
Abstract
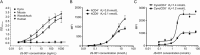
JS-001 is the first monoclonal antibody (mAb) against programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) approved by the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) into the clinical trails. To date, however, no pre-clinical pharmacological and pharmacokinetic (PK) data are available. In this study, we investigated the efficacy of JS-001 and conducted a preclinical PK study, including the monitoring of anti-drug antibodies (ADAs). We found that JS-001 specifically bound to PD-1 antigen with an EC50 of 21 nmol/L, and competently blocked the binding of PD-1 antigen to PD-L1 and PD-L2 with IC50 of 3.0 and 3.1 nmol/L, respectively. Furthermore, JS-001 displayed distinct species cross-reactivity: it could bind to the PD-1 antigen on the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of humans and cynomolgus monkeys, but not to those of mice and woodchucks; the Kd values for the interaction between JS-001 and PD-1 antigens on CD8+ T cells of human and cynomolgus monkey were 2.1 nmol/L and 1.2 nmol/L, respectively. In vitro, treatment with JS-001 (0.01-10 μg/mL) dose-dependently stimulated human T cell proliferation, as well as IFN-γ and TNF-α secretion. In HBsAg-vaccinated cynomolgus monkeys, the expression of PD-1+/CD4+ and PD-1+/CD8+ was significantly elevated, intramuscular injection of JS-001 (1 and 10 mg/kg) resulted in dramatic decreases in PD-1+/CD4+ and PD-1+/CD8+ expression in a dose-dependent manner, which was supported by PD-1 receptor occupancy (RO) results. In the PK study, 18 cynomolgus monkeys treated with single, ascending doses of 1, 10, and 75 mg/kg, and another 6 cynomolgus monkeys received 10 mg/kg successive administration. The plasma clearance of JS-001 followed a linear PK profile with single administration in the 1 and 10 mg/kg groups and a non-linear PK profile in the 75 mg/kg group. In the successive 10 mg/kg administration group, no drug accumulation was observed. But the AUC from the last exposure was lower than that of the first administration, which was probably due to the production of ADAs, as demonstrated in immunogenicity study. These non-clinical data are encouraging and provide a basis for the efficacy and safety of JS-001 in clinical trials.
Figures



References
-
- Rizvi NA, Mazières J, Planchard D, Stinchcombe TE, Dy GK, Antonia SJ, et al. Activity and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, for patients with advanced, refractory squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 063): a phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16: 257–65. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

