The Global Burden of Oral Disease: Research and Public Health Significance
- PMID: 28318392
- PMCID: PMC6728669
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034517693567
The Global Burden of Oral Disease: Research and Public Health Significance
Keywords: data mining; dental informatics; dental public health; epidemiology; global health; health services research.
Conflict of interest statement
The author received no financial support and declares no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures

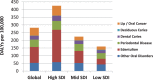
Comment on
-
Global, Regional, and National Prevalence, Incidence, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years for Oral Conditions for 195 Countries, 1990-2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors.J Dent Res. 2017 Apr;96(4):380-387. doi: 10.1177/0022034517693566. J Dent Res. 2017. PMID: 28792274 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GBD 2015 DALYs and HALE Collaborators. 2016. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 315 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE), 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 388(10053):1603–1658. - PMC - PubMed
-
- GBD 2015: from big data to meaningful change. 2016. Lancet. 388(10053):1447. - PubMed
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. 2016a. GBDCompareData Visualization. Seattle (WA): University of Washington; [accessed 2016 Nov 21]. http://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare.
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. 2016b. Rethinking development and health: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Seattle (WA): Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation.
-
- Kassebaum NJ, Smith AGC, Bernabé E, Fleming TD, Reynolds AE, Vos T, Murray CJL, Marcenes W, GBD 2015 Oral Health Collaborators. 2017. Global, regional, and national prevalence, incidence, and disability-adjusted life years for oral conditions for 195 countries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. J Dent Res. 96(4):380-387. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

