Metagenomic discovery of polybrominated diphenyl ether biosynthesis by marine sponges
- PMID: 28319100
- PMCID: PMC5391271
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.2330
Metagenomic discovery of polybrominated diphenyl ether biosynthesis by marine sponges
Abstract
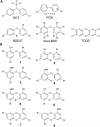
Naturally produced polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) pervade the marine environment and structurally resemble toxic man-made brominated flame retardants. PBDEs bioaccumulate in marine animals and are likely transferred to the human food chain. However, the biogenic basis for PBDE production in one of their most prolific sources, marine sponges of the order Dysideidae, remains unidentified. Here, we report the discovery of PBDE biosynthetic gene clusters within sponge-microbiome-associated cyanobacterial endosymbionts through the use of an unbiased metagenome-mining approach. Using expression of PBDE biosynthetic genes in heterologous cyanobacterial hosts, we correlate the structural diversity of naturally produced PBDEs to modifications within PBDE biosynthetic gene clusters in multiple sponge holobionts. Our results establish the genetic and molecular foundation for the production of PBDEs in one of the most abundant natural sources of these molecules, further setting the stage for a metagenomic-based inventory of other PBDE sources in the marine environment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Genomics of Cyanobacterial Symbionts Reveals Distinct, Specialized Metabolism in Tropical Dysideidae Sponges.mBio. 2019 May 14;10(3):e00821-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00821-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31088928 Free PMC article.
-
Trophic transfer of naturally produced brominated aromatic compounds in a Baltic Sea food chain.Chemosphere. 2016 Feb;144:1597-604. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.10.024. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Chemosphere. 2016. PMID: 26517387
-
Complexity of naturally produced polybrominated diphenyl ethers revealed via mass spectrometry.Environ Sci Technol. 2015 Feb 3;49(3):1339-46. doi: 10.1021/es505440j. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Environ Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 25559102 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Metagenomic Analysis of Biosynthetic Diversity across Sponge Microbiomes Highlights Metabolic Novelty, Conservation, and Diversification.mSystems. 2022 Aug 30;7(4):e0035722. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00357-22. Epub 2022 Jul 18. mSystems. 2022. PMID: 35862823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical review of soil contamination by polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs); concentrations, sources and congener profiles.Environ Pollut. 2017 Nov;230:741-757. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.009. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Environ Pollut. 2017. PMID: 28732337 Review.
Cited by
-
Mining genomes to illuminate the specialized chemistry of life.Nat Rev Genet. 2021 Sep;22(9):553-571. doi: 10.1038/s41576-021-00363-7. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Nat Rev Genet. 2021. PMID: 34083778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genomic view of trophic and metabolic diversity in clade-specific Lamellodysidea sponge microbiomes.Microbiome. 2020 Jun 23;8(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00877-y. Microbiome. 2020. PMID: 32576248 Free PMC article.
-
From Tryptophan to Toxin: Nature's Convergent Biosynthetic Strategy to Aetokthonotoxin.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Feb 23;144(7):2861-2866. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c12778. Epub 2022 Feb 10. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 35142504 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Ecology of Marine Sponges: New Opportunities through "-Omics".Integr Comp Biol. 2019 Oct 1;59(4):765-776. doi: 10.1093/icb/icz014. Integr Comp Biol. 2019. PMID: 30942859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances of Marine Sponge-Associated Microorganisms as a Source of Commercially Viable Natural Products.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2022 Jun;24(3):492-512. doi: 10.1007/s10126-022-10130-2. Epub 2022 May 14. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2022. PMID: 35567600 Review.
References
-
- Hites RA. Dioxins: an overview and history. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011;45:16–20. - PubMed
-
- Wiseman SB, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and their hydroxylated/methoxylated analogs: environmental sources, metabolic relationships, and relative toxicities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011;63:179–188. - PubMed
-
- Gribble GW. Naturally Occurring Organohalogen Compounds - A Comprehensive Update. Vol. 91. Springer; Vienna: 2010.
-
- Sharma GM, Vig B. Studies on the antimicrobial substances of sponges. VI. Structures of two antibacterial substances isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea herbacea. Tetrahedron Lett. 1972;13:1715–1718.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- PubChem-Substance/329729822
- PubChem-Substance/329729825
- PubChem-Substance/329729826
- PubChem-Substance/329729827
- PubChem-Substance/329729828
- PubChem-Substance/329729829
- PubChem-Substance/329729830
- PubChem-Substance/329729831
- PubChem-Substance/329729832
- PubChem-Substance/329729823
- PubChem-Substance/329729824
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

