An alpha-synuclein MRM assay with diagnostic potential for Parkinson's disease and monitoring disease progression
- PMID: 28319654
- PMCID: PMC5540649
- DOI: 10.1002/prca.201700045
An alpha-synuclein MRM assay with diagnostic potential for Parkinson's disease and monitoring disease progression
Abstract
Aim: The alpha-synuclein (α-syn) level in human cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), as measured by immunoassays, is promising as a Parkinson's disease (PD) biomarker. However, the levels of total α-syn are inconsistent among studies with large cohorts and different measurement platforms. Total α-syn level also does not correlate with disease severity or progression. Here, the authors developed a highly sensitive MRM method to measure absolute CSF α-syn peptide concentrations without prior enrichment or fractionation, aiming to discover new candidate biomarkers.
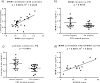
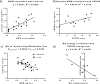
Results: Six peptides covering 73% of protein sequence were reliably identified, and two were consistently quantified in cross-sectional and longitudinal cohorts. Absolute concentration of α-syn in human CSF was determined to be 2.1 ng/mL. A unique α-syn peptide, TVEGAGSIAAATGFVK (81-96), displayed excellent correlation with previous immunoassay results in two independent PD cohorts (p < 0.001), correlated with disease severity, and its changes significantly tracked the disease progression longitudinally.
Conclusions: An MRM assay to quantify human CSF α-syn was developed and optimized. Sixty clinical samples from cross-sectional and longitudinal PD cohorts were analyzed with this approach. Although further larger scale validation is needed, the results suggest that α-syn peptide could serve as a promising biomarker in PD diagnosis and progression.
Keywords: Diagnosis; MRM; Parkinson's disease; Progression; alpha-synuclein (α-syn).
© 2017 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amyloid-β and α-synuclein cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and cognition in early Parkinson's disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015 Jul;21(7):758-64. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.04.027. Epub 2015 May 2. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015. PMID: 25971633
-
Alpha-Synuclein Protofibrils in Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Potential Biomarker for Parkinson's Disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2020;10(4):1429-1442. doi: 10.3233/JPD-202141. J Parkinsons Dis. 2020. PMID: 33016895
-
Oligomeric and phosphorylated alpha-synuclein as potential CSF biomarkers for Parkinson's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2016 Jan 19;11:7. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0072-9. Mol Neurodegener. 2016. PMID: 26782965 Free PMC article.
-
Biological confounders for the values of cerebrospinal fluid proteins in Parkinson's disease and related disorders.J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139 Suppl 1:290-317. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13390. Epub 2016 Feb 10. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 26452984 Review.
-
Value of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein species as biomarker in Parkinson's diagnosis and prognosis.Biomark Med. 2016;10(1):35-49. doi: 10.2217/bmm.15.107. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Biomark Med. 2016. PMID: 26643452 Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Total, Phosphorylated and Oligomeric A-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression Study.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 5;12(10):2266. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102266. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics Challenges for the Assessment of Synuclein Proteoforms as Clinical Biomarkers in Parkinson's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 31;14:818606. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.818606. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35431896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthetic homeostasis and resilience of the complement system in health and infectious disease.EBioMedicine. 2019 Jul;45:303-313. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.06.008. Epub 2019 Jun 29. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31262714 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry and Tandem Collision Induced Unfolding for Quantification of Elusive Protein Biomarkers.Anal Chem. 2024 Apr 16;96(15):6021-6029. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c00477. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38557001 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry for Neurobiomarker Discovery: The Relevance of Post-Translational Modifications.Cells. 2022 Apr 9;11(8):1279. doi: 10.3390/cells11081279. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35455959 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hall S, Ohrfelt A, Constantinescu R, Andreasson U, et al. Accuracy of a panel of 5 cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the differential diagnosis of patients with dementia and/or parkinsonian disorders. Archives of neurology. 2012;69:1445–1452. - PubMed
-
- Mollenhauer B, Locascio JJ, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Sixel-Doring F, et al. alpha-Synuclein and tau concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of patients presenting with parkinsonism: a cohort study. The Lancet Neurology. 2011;10:230–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

