Myeloid p53 regulates macrophage polarization and venous thrombus resolution by inflammatory vascular remodeling in mice
- PMID: 28320710
- PMCID: PMC5472897
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-07-727180
Myeloid p53 regulates macrophage polarization and venous thrombus resolution by inflammatory vascular remodeling in mice
Abstract
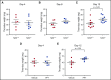
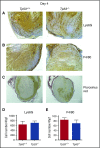
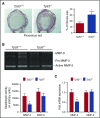
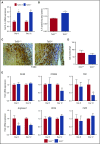
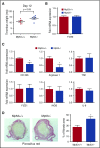
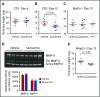
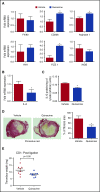
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) remains a common and serious cardiovascular problem with both fatal and long-term consequences. The consequences of DVT include the development of postthrombotic syndrome in 25% to 60% of DVT patients. Despite the clinical importance of venous thrombus resolution, the cellular and molecular mediators involved are poorly understood, and currently there is no molecular therapy to accelerate this process. Several lines of evidence suggest that a complex and interrelated array of molecular signaling processes are involved in the inflammatory vascular remodeling associated with the resolution of DVT. Here, we have identified a role for the tumor suppressor gene p53 in regulating venous thrombus resolution. Using the stasis model of venous thrombosis and resolution in mice, we found that genetic deficiency of p53 or pharmacologic inhibition by pifithrin impairs thrombus resolution and is associated with increased fibrosis and altered expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2. The effect of p53 loss was mediated by cells of the myeloid lineage, resulting in enhanced polarization of the cytokine milieu toward an M1-like phenotype. Furthermore, augmentation of p53 activity using the pharmacological agonist of p53, quinacrine, accelerates venous thrombus resolution in a p53-dependent manner, even after establishment of thrombosis. Together, these studies define mechanisms by which p53 regulates thrombus resolution by increasing inflammatory vascular remodeling of venous thrombi in vivo, and the potential therapeutic application of a p53 agonist as a treatment to accelerate this process in patients with DVT.
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
Comment in
-
From tumor suppressor to thrombus resolver.Blood. 2017 Jun 15;129(24):3144-3145. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-04-776401. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28620104 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hirsh J, Lee AY. How we diagnose and treat deep vein thrombosis. Blood. 2002;99(9):3102-3110. - PubMed
-
- Lee AY, Hirsh J. Diagnosis and treatment of venous thromboembolism. Annu Rev Med. 2002;53:15-33. - PubMed
-
- Kearon C. Long-term management of patients after venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2004;110(9 suppl 1):I10-I18. - PubMed
-
- Prandoni P, Noventa F, Lensing AW, Prins MH, Villalta S. Post-thrombotic syndrome and the risk of subsequent recurrent thromboembolism. Thromb Res. 2016;141:91-92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

