ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation
- PMID: 28321223
- PMCID: PMC5338156
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00234
ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation
Abstract
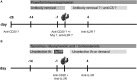
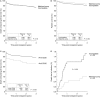
ABO-incompatible (ABOi) kidney transplantation has long been considered a contraindication to successful kidney transplantation. During the last 25 years, increasing organ shortage enforced the development of strategies to overcome the ABO antibody barrier. In the meantime, ABOi kidney transplantation has become a routine procedure with death-censored graft survival rates comparable to the rates in compatible transplantations. Desensitization is usually achieved by apheresis and B cell-depleting therapies that are accompanied by powerful immunosuppression. Anti-A/B antibodies are aimed to be below a certain threshold at the time of ABOi kidney transplantation and during the first 2 weeks after surgery. Thereafter, even a rebound of anti-A/B antibodies does not appear to harm the kidney transplant, a phenomenon that is called accommodation, but is poorly understood. There is still concern, however, that infectious complications such as viral disease, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, and severe urinary tract infections are increased after ABOi transplantations. Recent data from the Collaborative Transplant Study show that during the first year after kidney transplantation, one additional patient death from an infectious complication occurs in 100 ABOi kidney transplant recipients. Herein, we review the recent evidence on ABOi kidney transplantation with a focus on desensitization strategies and respective outcomes.
Keywords: ABO incompatible; antibodies; desensitization; kidney transplantation; survival.
Figures
References
-
- Alexandre GP, De Bruyere M, Squifflet JP, Moriau M, Latinne D, Pirson Y. Human ABO-incompatible living donor renal homografts. Neth J Med (1985) 28(6):231–4. - PubMed
-
- Squifflet JP, De Meyer M, Malaise J, Latinne D, Pirson Y, Alexandre GP. Lessons learned from ABO-incompatible living donor kidney transplantation: 20 years later. Exp Clin Transplant (2004) 2(1):208–13. - PubMed
-
- Rydberg L, Breimer ME, Samuelsson BE, Brynger H. Blood group ABO-incompatible (A2 to O) kidney transplantation in human subjects: a clinical, serologic, and biochemical approach. Transplant Proc (1987) 19(6):4528–37. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

