Salivary Distinctiveness and Modifications in Males with Diabetes and Behçet's Disease
- PMID: 28321337
- PMCID: PMC5339495
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9596202
Salivary Distinctiveness and Modifications in Males with Diabetes and Behçet's Disease
Abstract
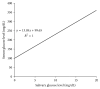
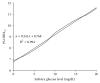
Oral diseases associated with systematic diseases as metabolic and vasculitic have been included in this paper. This will enhance our understanding of the salivary function in promoting healthy oral condition. The study investigates the effects of type I and type II diabetes mellitus in well-controlled diabetic patients, in addition to Behçet disease (BD) on saliva flow rate (SFR), pH, the decay, missing, and filled tooth (DMFT) index, glucose, and major earth-alkaline ions (Ca2+ and Mg2+) compared to healthy males and age-matched controls. Saliva samples were collected from 1403 male human subjects, distributed on 7 levels including 3 control groups, and analyzed. The symptoms and clinical observations were enrolled. A preprandial salivary glucose has illustrated statistically strong significant and positive correlations with HbA1c and blood glucose levels. TIDM saliva showed lower pH, SFR, and Ca2+ but higher Mg2+, caries risk, and poor metabolic control. These led to dysfunction of secretory capacity of salivary glands. TIIDM proved higher SFR, DMFT, and glucose than TIDM patients. DM oral calcium has decreased by age while magnesium sharply slopes at seniority. BD oral fluid is associated with lower glucose and minerals but noticeably with both higher pH and DMFT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Mandel I. D. Salivary diagnosis: more than a lick and a promise. The Journal of the American Dental Association. 1993;124(2):85–87. - PubMed
-
- Lasisi T. J., Fasanmade A. A. Salivary flow and composition in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. Nigerian Journal of Physiological Sciences. 2012;27(1):79–82. - PubMed
-
- Twetman S., Johansson I., Birkhed D., Nederfors T. Dental caries-associated risk factors and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatric Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism. 2001;17(3):152–157. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous