Treatment Outcomes of Rathke's Cleft Cysts Managed with Marsupialization
- PMID: 28321372
- PMCID: PMC5357223
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1585088
Treatment Outcomes of Rathke's Cleft Cysts Managed with Marsupialization
Abstract
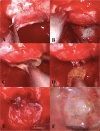
Objectives Rathke's cleft cysts (RCC) are benign cystic lesions of the sella resulting from incomplete obliteration of Rathke's cleft. Symptomatic lesions often require surgical decompression, which is often amenable to a transnasal, transsphenoidal (TNTS) approach. We report our experience with marsupialization of RCC and describe a novel technique to promote re-epithelization of the cyst cavity. Design Retrospective review. Setting Tertiary academic medical center. Participants Patients who underwent TNTS for RCC between 2007 and 2015. Main Outcome Measures Demographics, lesion characteristics, and reconstruction and treatment outcomes. Results In total, 52 patients were identified. The mean age was 41 ± 18 years. The mean RCC size was 13 ± 5 mm. Intraoperative cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak was encountered in 14 (27%) patients; all were repaired. There were six complications (12%) and no deaths. Mean follow-up was 20 ± 18 months, with five (10%) recurrences. RCC size was associated with intraoperative CSF leak (p = 0.04). In 12 patients, the marsupialized cyst cavity was lined with a free mucosal graft (FMG) to promote healing and re-epithelialization. Conclusions The TNTS approach is safe and effective in surgical decompression of RCC. Lining the exposed cyst cavity with an FMG is a simple intervention without added morbidity that may promote formation of an epithelialized tract. Level of Evidence Not applicable.
Keywords: Rathke's cleft cyst; free mucosal grafting; marsupialization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Teramoto A, Hirakawa K, Sanno N, Osamura Y. Incidental pituitary lesions in 1,000 unselected autopsy specimens. Radiology. 1994;193(1):161–164. - PubMed
-
- Ross D A Norman D Wilson C B Radiologic characteristics and results of surgical management of Rathke's cysts in 43 patients Neurosurgery 1992302173–178., discussion 178–179 - PubMed
-
- Guo S Y, Cai X Q, Ma J, Wang W Y, Lu G. Diagnosis of concomitant pituitary adenoma and Rathke's cleft cyst with magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Surg. 2015;18:191–195. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda H, Ohhashi G. Demonstration of high coincidence of pituitary adenoma in patients with ruptured Rathke's cleft cyst: results of a prospective study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;139:144–151. - PubMed
-
- Fager C A, Carter H. Intrasellar epithelial cysts. J Neurosurg. 1966;24(1):77–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

