Colony, hanging drop, and methylcellulose three dimensional hypoxic growth optimization of renal cell carcinoma cell lines
- PMID: 28321776
- PMCID: PMC5507837
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-016-0063-2
Colony, hanging drop, and methylcellulose three dimensional hypoxic growth optimization of renal cell carcinoma cell lines
Abstract
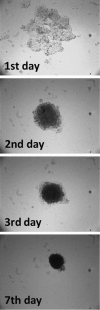
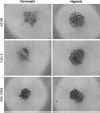
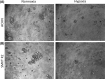
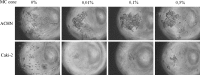
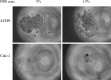
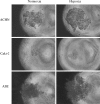
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most lethal of the common urologic malignancies, comprising 3% of all human neoplasms, and the incidence of kidney cancer is rising annually. We need new approaches to target tumor cells that are resistant to current therapies and that give rise to recurrence and treatment failure. In this study, we focused on low oxygen tension and three-dimensional (3D) cell culture incorporation to develop a new RCC growth model. We used the hanging drop and colony formation methods, which are common in 3D culture, as well as a unique methylcellulose (MC) method. For the experiments, we used human primary RCC cell lines, metastatic RCC cell lines, human kidney cancer stem cells, and human healthy epithelial cells. In the hanging drop assay, we verified the potential of various cell lines to create solid aggregates in hypoxic and normoxic conditions. With the semi-soft agar method, we also determined the ability of various cell lines to create colonies under different oxygen conditions. Different cell behavior observed in the MC method versus the hanging drop and colony formation assays suggests that these three assays may be useful to test various cell properties. However, MC seems to be a particularly valuable alternative for 3D cell culture, as its higher efficiency of aggregate formation and serum independency are of interest in different areas of cancer biology.
Keywords: Colony; Hanging drop; Hypoxia; Methylcellulose; RCC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative Gene Expression Profiling of Primary and Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Stem Cell-Like Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 3;11(11):e0165718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165718. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27812180 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic 3D in vitro culture models reveal distinct resistance processes to TKIs in renal cancer cells.Cell Biosci. 2017 Dec 16;7:71. doi: 10.1186/s13578-017-0197-8. eCollection 2017. Cell Biosci. 2017. PMID: 29270287 Free PMC article.
-
Redifferentiation of in vitro expanded adult articular chondrocytes by combining the hanging-drop cultivation method with hypoxic environment.Cell Transplant. 2008;17(8):987-96. doi: 10.3727/096368908786576499. Cell Transplant. 2008. PMID: 19069640
-
Novel approaches in the therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma.World J Urol. 2005 Jul;23(3):202-12. doi: 10.1007/s00345-004-0466-0. Epub 2005 Apr 5. World J Urol. 2005. PMID: 15812574 Review.
-
Precancerous lesions in the kidney.Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 2000;(205):136-65. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 2000. PMID: 11144893 Review.
Cited by
-
Fabrication of a Three-Dimensional Spheroid Culture System for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Using a Microfabricated Device.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 26;15(21):5162. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215162. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958336 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial drug screening on 3D Ewing sarcoma spheroids using droplet-based microfluidics.iScience. 2023 Apr 12;26(5):106651. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106651. eCollection 2023 May 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37168549 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of the capacity of mesenchymal stromal cell lines to form spheroids.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 2;15(6):e0225485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225485. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32484831 Free PMC article.
-
Looking into the Eyes-In Vitro Models for Ocular Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 15;23(16):9158. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169158. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maintenance of viability and proliferation of 3T3 cell aggregates incorporating fibroin microspheres into cultures.Cytotechnology. 2020 Aug;72(4):579-587. doi: 10.1007/s10616-020-00408-5. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Cytotechnology. 2020. PMID: 32797335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altmann B, Steinberg T, Giselbrecht S, Gottwald E, Tomakidi P, Bachle-Haas M, Kohal RJ. Promotion of osteoblast differentiation in 3D biomaterial micro-chip arrays comprising fibronectin-coated poly(methyl methacrylate) polycarbonate. Biomaterials. 2011;32(34):8947–8956. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ami Y, Shimazui T, Akaza H, Uematsu N, Yano Y, Tsujimoto G, Uchida K. Gene expression profiles correlate with the morphology and metastasis characteristics of renal cell carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2005;13(1):75–80. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KM, Guinan P, Rubenstein M. The effect of normoxia and hypoxia on a prostate (PC-3) CD44/CD41 cell side fraction. Anticancer Res. 2011;31(2):487–494. - PubMed
-
- Arai E, Ushijima S, Tsuda H, Fujimoto H, Hosoda F, Shibata T, Kondo T, Imoto I, Inazawa J, Hirohashi S, et al. Genetic clustering of clear cell renal cell carcinoma based on array-comparative genomic hybridization: its association with DNA methylation alteration and patient outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(17):5531–5539. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0443. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

