Spin-lock imaging of exogenous exchange-based contrast agents to assess tissue pH
- PMID: 28321903
- PMCID: PMC6889218
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.26681
Spin-lock imaging of exogenous exchange-based contrast agents to assess tissue pH
Abstract
Purpose: Some X-ray contrast agents contain exchangeable protons that give rise to exchange-based effects on MRI, including chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST). However, CEST has poor specificity to explicit exchange parameters. Spin-lock sequences at high field are also sensitive to chemical exchange. Here, we evaluate whether spin-locking techniques can detect the contrast agent iohexol in vivo after intravenous administration, and their potential for measuring changes in tissue pH.
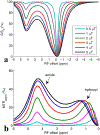
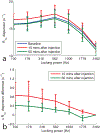
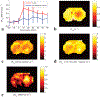
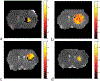
Methods: Two metrics of contrast based on R1ρ , the spin lattice relaxation rate in the rotating frame, were derived from the behavior of R1ρ at different locking fields. Solutions containing iohexol at different concentrations and pH were used to evaluate the ability of the two metrics to quantify exchange effects. Images were also acquired from rat brains bearing tumors before and after intravenous injections of iohexol to evaluate the potential of spin-lock techniques for detecting the agent and pH variations.
Results: The two metrics were found to depend separately on either agent concentration or pH. Spin-lock imaging may therefore provide specific quantification of iohexol concentration and the iohexol-water exchange rate, which reports on pH.
Conclusions: Spin-lock techniques may be used to assess the dynamics of intravenous contrast agents and detect extracellular acidification. Magn Reson Med 79:298-305, 2018. © 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Keywords: MRI; X-ray agent; extracellular pH; spin lock.
© 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Spin-lock imaging of early tissue pH changes in ischemic rat brain.NMR Biomed. 2018 Apr;31(4):e3893. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3893. Epub 2018 Feb 9. NMR Biomed. 2018. PMID: 29424463 Free PMC article.
-
Exchange-mediated contrast agents for spin-lock imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2012 May;67(5):1427-33. doi: 10.1002/mrm.23130. Epub 2011 Sep 27. Magn Reson Med. 2012. PMID: 21954094 Free PMC article.
-
Exchange-mediated contrast in CEST and spin-lock imaging.Magn Reson Imaging. 2014 Jan;32(1):28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24239335 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into rotating frame relaxation at high field.NMR Biomed. 2016 Sep;29(9):1258-73. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3490. Epub 2016 Feb 11. NMR Biomed. 2016. PMID: 26866422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of optimization and quantification techniques for chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI toward sensitive in vivo imaging.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2015 May-Jun;10(3):163-178. doi: 10.1002/cmmi.1628. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25641791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging tumor acidosis: a survey of the available techniques for mapping in vivo tumor pH.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019 Jun;38(1-2):25-49. doi: 10.1007/s10555-019-09782-9. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019. PMID: 30762162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AcidoCEST-UTE MRI for the Assessment of Extracellular pH of Joint Tissues at 3 T.Invest Radiol. 2019 Sep;54(9):565-571. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000576. Invest Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31107700 Free PMC article.
-
Spin-lock imaging of early tissue pH changes in ischemic rat brain.NMR Biomed. 2018 Apr;31(4):e3893. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3893. Epub 2018 Feb 9. NMR Biomed. 2018. PMID: 29424463 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of APT using a combined CERT-AREX approach with varying duty cycles.Magn Reson Imaging. 2017 Oct;42:22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 May 17. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28526431 Free PMC article.
-
Correction of errors in estimates of T1ρ at low spin-lock amplitudes in the presence of B0 and B1 inhomogeneities.NMR Biomed. 2023 Apr 17:e4951. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4951. Online ahead of print. NMR Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37070215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dawson P. Chemotoxicity of Contrast-Media and Clinical Adverse-Effects - a Review. Investigative Radiology 1985;20(1):S84–S91. - PubMed
-
- Schrott KM, Behrends B, Clauss W, Kaufmann J, Lehnert J. Iohexol in Excretory Urography - Results of the Drug-Monitoring Program. Fortschritte Der Medizin 1986;104(7):153–156. - PubMed
-
- Aime S, Nano R, Grandi M. A New Class of Contrast Agents for Magnetic-Resonance Imaging Based on Selective Reduction of Water-T2 by Chemical-Exchange. Investigative Radiology 1988;23:S267–S270. - PubMed
-
- Longo DL, Michelotti F, Consolino L, Bardini P, Digilio G, Xiao G, Sun PZ, Aime S. In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment of Nonionic Iodinated Radiographic Molecules as Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging Tumor Perfusion Agents. Investigative Radiology 2016;51(3):155–162. - PubMed
-
- Aime S, Calabi L, Biondi L, De Miranda M, Ghelli S, Paleari L, Rebaudengo C, Terreno E. Iopamidol: Exploring the potential use of a well-established X-ray contrast agent for MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2005;53(4):830–834. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

