Spin-lock imaging of exogenous exchange-based contrast agents to assess tissue pH
- PMID: 28321903
- PMCID: PMC6889218
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.26681
Spin-lock imaging of exogenous exchange-based contrast agents to assess tissue pH
Abstract
Purpose: Some X-ray contrast agents contain exchangeable protons that give rise to exchange-based effects on MRI, including chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST). However, CEST has poor specificity to explicit exchange parameters. Spin-lock sequences at high field are also sensitive to chemical exchange. Here, we evaluate whether spin-locking techniques can detect the contrast agent iohexol in vivo after intravenous administration, and their potential for measuring changes in tissue pH.
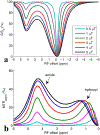
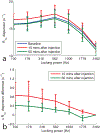
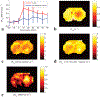
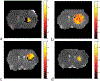
Methods: Two metrics of contrast based on R1ρ , the spin lattice relaxation rate in the rotating frame, were derived from the behavior of R1ρ at different locking fields. Solutions containing iohexol at different concentrations and pH were used to evaluate the ability of the two metrics to quantify exchange effects. Images were also acquired from rat brains bearing tumors before and after intravenous injections of iohexol to evaluate the potential of spin-lock techniques for detecting the agent and pH variations.
Results: The two metrics were found to depend separately on either agent concentration or pH. Spin-lock imaging may therefore provide specific quantification of iohexol concentration and the iohexol-water exchange rate, which reports on pH.
Conclusions: Spin-lock techniques may be used to assess the dynamics of intravenous contrast agents and detect extracellular acidification. Magn Reson Med 79:298-305, 2018. © 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Keywords: MRI; X-ray agent; extracellular pH; spin lock.
© 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures


References
-
- Dawson P. Chemotoxicity of Contrast-Media and Clinical Adverse-Effects - a Review. Investigative Radiology 1985;20(1):S84–S91. - PubMed
-
- Schrott KM, Behrends B, Clauss W, Kaufmann J, Lehnert J. Iohexol in Excretory Urography - Results of the Drug-Monitoring Program. Fortschritte Der Medizin 1986;104(7):153–156. - PubMed
-
- Aime S, Nano R, Grandi M. A New Class of Contrast Agents for Magnetic-Resonance Imaging Based on Selective Reduction of Water-T2 by Chemical-Exchange. Investigative Radiology 1988;23:S267–S270. - PubMed
-
- Longo DL, Michelotti F, Consolino L, Bardini P, Digilio G, Xiao G, Sun PZ, Aime S. In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment of Nonionic Iodinated Radiographic Molecules as Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging Tumor Perfusion Agents. Investigative Radiology 2016;51(3):155–162. - PubMed
-
- Aime S, Calabi L, Biondi L, De Miranda M, Ghelli S, Paleari L, Rebaudengo C, Terreno E. Iopamidol: Exploring the potential use of a well-established X-ray contrast agent for MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2005;53(4):830–834. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

