Genomic changes following the reversal of a Y chromosome to an autosome in Drosophila pseudoobscura
- PMID: 28322435
- PMCID: PMC5485016
- DOI: 10.1111/evo.13229
Genomic changes following the reversal of a Y chromosome to an autosome in Drosophila pseudoobscura
Abstract
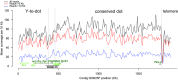
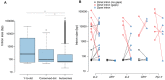
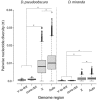
Robertsonian translocations resulting in fusions between sex chromosomes and autosomes shape karyotype evolution by creating new sex chromosomes from autosomes. These translocations can also reverse sex chromosomes back into autosomes, which is especially intriguing given the dramatic differences between autosomes and sex chromosomes. To study the genomic events following a Y chromosome reversal, we investigated an autosome-Y translocation in Drosophila pseudoobscura. The ancestral Y chromosome fused to a small autosome (the dot chromosome) approximately 10-15 Mya. We used single molecule real-time sequencing reads to assemble the D. pseudoobscura dot chromosome, including this Y-to-dot translocation. We find that the intervening sequence between the ancestral Y and the rest of the dot chromosome is only ∼78 Kb and is not repeat-dense, suggesting that the centromere now falls outside, rather than between, the fused chromosomes. The Y-to-dot region is 100 times smaller than the D. melanogaster Y chromosome, owing to changes in repeat landscape. However, we do not find a consistent reduction in intron sizes across the Y-to-dot region. Instead, deletions in intergenic regions and possibly a small ancestral Y chromosome size may explain the compact size of the Y-to-dot translocation.
Keywords: Dot chromosome; Robertsonian translocation; SMRT sequencing; Y chromosome.
© 2017 The Author(s). Evolution published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Society for the Study of Evolution.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Y chromosome of D. pseudoobscura is not homologous to the ancestral Drosophila Y.Science. 2005 Jan 7;307(5706):108-10. doi: 10.1126/science.1101675. Epub 2004 Nov 4. Science. 2005. PMID: 15528405
-
Complex Evolutionary History of the Y Chromosome in Flies of the Drosophila obscura Species Group.Genome Biol Evol. 2020 May 1;12(5):494-505. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaa051. Genome Biol Evol. 2020. PMID: 32176296 Free PMC article.
-
Translocation of Y-linked genes to the dot chromosome in Drosophila pseudoobscura.Mol Biol Evol. 2010 Jul;27(7):1612-20. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq045. Epub 2010 Feb 10. Mol Biol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20147437 Free PMC article.
-
Non-random autosome segregation: a stepping stone for the evolution of sex chromosome complexes? Sex-biased transmission of autosomes could facilitate the spread of antagonistic alleles, and generate sex-chromosome systems with multiple X or Y chromosomes.Bioessays. 2011 Feb;33(2):111-4. doi: 10.1002/bies.201000106. Bioessays. 2011. PMID: 21154781 Review.
-
Origin and evolution of Y chromosomes: Drosophila tales.Trends Genet. 2009 Jun;25(6):270-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2009.04.002. Epub 2009 May 13. Trends Genet. 2009. PMID: 19443075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neo-sex Chromosomes in the Monarch Butterfly, Danaus plexippus.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Oct 5;7(10):3281-3294. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.300187. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28839116 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and evolution of heterochromatin.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020 Sep;1476(1):59-77. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14303. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020. PMID: 32017156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A germline PAF1 paralog complex ensures cell type-specific gene expression.Genes Dev. 2024 Oct 16;38(17-20):866-886. doi: 10.1101/gad.351930.124. Genes Dev. 2024. PMID: 39332828 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evolution of Drosophila chromatin landscape in a 3D genome context.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 1;15(1):9452. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53892-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39487148 Free PMC article.
-
Satellite DNA-containing gigantic introns in a unique gene expression program during Drosophila spermatogenesis.PLoS Genet. 2019 May 9;15(5):e1008028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008028. eCollection 2019 May. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31071079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abad, J. P. , de Pablos B., Agudo M., Molina I., Giovinazzo G., Martin‐Gallardo A., and Villasante A.. 2004. Genomic and cytological analysis of the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster: telomere‐derived sequences at internal regions. Chromosoma 113:295–304. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F. , Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., and Lipman D. J.. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403–410. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
