Clinicopathological and prognostic features of surgically resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma harboring epidermal growth factor receptor and K-ras mutation
- PMID: 28322512
- PMCID: PMC5415485
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12428
Clinicopathological and prognostic features of surgically resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma harboring epidermal growth factor receptor and K-ras mutation
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to evaluate mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and K-ras genes and their clinicopathological and prognostic features in patients with resected pathological stage I adenocarcinoma.
Methods: We examined 224 patients with surgically resected lung adenocarcinoma and analyzed the prognostic and predictive value of these mutations in 162 patients with pathological stage I adenocarcinoma.
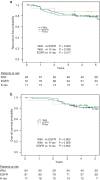
Results: Mutations of the EGFR and K-ras genes were detected in 100 (44.6%) and 19 (8.5%) of all tumors, and in 81 (50.0%) and 17 (10.5%) of the pathological stage I tumors, respectively. EGFR mutations were significantly associated with female gender, smoking habit (never smoker), and low grade. By contrast, K-ras mutations were significantly associated with male gender, smoking habit (ever smoker), and the presence of mucinous components. No significant differences were observed in recurrence-free or overall survival between the EGFR-mutant, K-ras-mutant, and wild-type groups (five-year recurrence-free survival 77.8% vs. 87.8% vs. 79.5%; five-year overall survival 82.8% vs. 82.4% vs. 79.2%, respectively). Multivariate analysis showed that neither EGFR nor K-ras mutation was an independent prognostic factor.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrated that pathological stage I adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR and K-ras gene mutations have distinct clinicopathological features. The presence of these mutations alone were not prognostic factors in patients with resected pathological stage I adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma; K-ras; epidermal growth factor receptor.
© 2017 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutations of the EGFR, K-ras, EML4-ALK, and BRAF genes in resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma.Surg Today. 2016 Sep;46(9):1091-8. doi: 10.1007/s00595-015-1295-z. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Surg Today. 2016. PMID: 26711128
-
KRAS Mutation Is a Significant Prognostic Factor in Early-stage Lung Adenocarcinoma.Am J Surg Pathol. 2016 Dec;40(12):1579-1590. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000744. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27740967 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations of the EGFR and K-ras genes in resected stage I lung adenocarcinoma and their clinical significance.Surg Today. 2014 Mar;44(3):478-86. doi: 10.1007/s00595-013-0589-2. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Surg Today. 2014. PMID: 23609009
-
Prognostic factors for resected invasive mucinous lung adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2024 Oct 25;24(1):1317. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13068-x. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39455981 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of the systemic immune-inflammation index in brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma with different EGFR mutations.Genes Immun. 2019 Jul;20(6):455-461. doi: 10.1038/s41435-018-0050-z. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Genes Immun. 2019. PMID: 30410015 Review.
Cited by
-
Significance of the epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status and differences among molecular subgroups in surgically resected lung microinvasive adenocarcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2018 Dec;16(6):7057-7067. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9539. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30546439 Free PMC article.
-
The Significance of MMP-1 in EGFR-TKI-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma: Potential for Therapeutic Targeting.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 18;19(2):609. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020609. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29463039 Free PMC article.
-
Correction to: Prognostic significance of preoperative plasma D-dimer level in patients with surgically resected clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective cohort study.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019 Jun 20;14(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13019-019-0935-6. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31221171 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of EGFR and KRAS in resected non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Sep 10;10:3393-3404. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S167578. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30237741 Free PMC article.
-
Depicting growth characteristics with computed tomography for KRAS-mutated lung adenocarcinoma.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 May 1;15(5):3942-3949. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-1880. Epub 2025 Apr 27. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40384723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sheel AR, McShane J, Poullis MP. Survival of patients with or without symptoms undergoing potentially curative resections for primary lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 2013; 95: 276–84. - PubMed
-
- Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC et al. Paclitaxel‐carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non‐small‐cell lung cancer. (Published erratum appears in N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 318.) N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2542–50. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Heigener DF, Mok T, Soria JC, Rabe KF. Management of non‐small‐cell lung cancer: Recent developments. Lancet 2013; 382: 709–19. - PubMed
-
- Yang JC, Wu YL, Schuler M et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin‐based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation‐positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX‐Lung 3 and LUX‐Lung 6): Analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16: 141–51. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non‐small‐cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2129–39. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

