Typhus Group Rickettsiosis, Texas, USA, 2003-2013
- PMID: 28322701
- PMCID: PMC5367421
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2304.160958
Typhus Group Rickettsiosis, Texas, USA, 2003-2013
Abstract
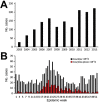
We characterized the epidemiology of typhus group rickettsiosis in Texas, USA. During 2003-2013, a total of 1,762 cases were reported to the state health department. The number of diagnosed cases and geographic expansion increased over time. Physician awareness is critical to diagnose and effectively treat rickettsial infections.
Keywords: Texas; Typhus group; United States; bacteria; fleas; murine typhus; rickettsia; rickettsiosis; vector-borne infections; zoonoses.
Figures

References
-
- Farhang Azad A, Traub R. Transmission of murine typhus rickettsiae by Xenopsylla cheopis, with notes on experimental infection and effects of temperature. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985;34:555–63. - PubMed
-
- Sorvillo FJ, Gondo B, Emmons R, Ryan P, Waterman SH, Tilzer A, et al. A suburban focus of endemic typhus in Los Angeles County: association with seropositive domestic cats and opossums. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1993;48:269–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

