Potential role of CYP1B1 in the development and treatment of metabolic diseases
- PMID: 28322972
- PMCID: PMC5600638
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.03.007
Potential role of CYP1B1 in the development and treatment of metabolic diseases
Abstract
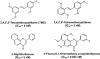
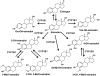
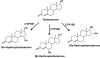
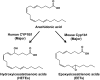
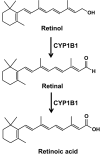
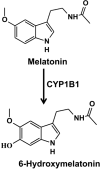
Cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1), a member of CYP superfamily, is expressed in liver and extrahepatic tissues carries out the metabolism of numerous xenobiotics, including metabolic activation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Surprisingly, CYP1B1 was also shown to be important in regulating endogenous metabolic pathways, including the metabolism of steroid hormones, fatty acids, melatonin, and vitamins. CYP1B1 and nuclear receptors including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), estrogen receptor (ER), and retinoic acid receptors (RAR) contribute to the maintenance of the homeostasis of these endogenous compounds. Many natural flavonoids and synthetic stilbenes show inhibitory activity toward CYP1B1 expression and function, notably isorhamnetin and 2,4,3',5'-tetramethoxystilbene. Accumulating evidence indicates that modulation of CYP1B1 can decrease adipogenesis and tumorigenesis, and prevent obesity, hypertension, atherosclerosis, and cancer. Therefore, it may be feasible to consider CYP1B1 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of metabolic diseases.
Keywords: CYP1B1; Metabolic diseases; Metabolic pathways; Metabolomics.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abe M, Itoh MT, Miyata M, Ishikawa S, Sumi Y. Detection of melatonin, its precursors and related enzyme activities in rabbit lens. Exp Eye Res. 1999;68:255–262. - PubMed
-
- Ajayi AA, Mathur R, Halushka PV. Testosterone increases human platelet thromboxane A2 receptor density and aggregation responses. Circulation. 1995;91:2742–2747. - PubMed
-
- Bejjani BA, Lewis RA, Tomey KF, Anderson KL, Dueker DK, Jabak M, Astle WF, Otterud B, Leppert M, Lupski JR. Mutations in CYP1B1, the gene for cytochrome P4501B1, are the predominant cause of primary congenital glaucoma in Saudi Arabia. American Journal of Human Genetics. 1998;62:325–333. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buters J, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Schober W, Soballa VJ, Hintermair J, Wolff T, Gonzalez FJ, Greim H. CYP1B1 determines susceptibility to low doses of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced ovarian cancers in mice: correlation of CYP1B1-mediated DNA adducts with carcinogenicity. Carcinogenesis. 2003;24:327–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

