Selective stalling of human translation through small-molecule engagement of the ribosome nascent chain
- PMID: 28323820
- PMCID: PMC5360235
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2001882
Selective stalling of human translation through small-molecule engagement of the ribosome nascent chain
Erratum in
-
Correction: Selective stalling of human translation through small-molecule engagement of the ribosome nascent chain.PLoS Biol. 2018 Apr 17;16(4):e1002628. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002628. eCollection 2018 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2018. PMID: 29664898 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) plays a key role in regulating the levels of plasma low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Here, we demonstrate that the compound PF-06446846 inhibits translation of PCSK9 by inducing the ribosome to stall around codon 34, mediated by the sequence of the nascent chain within the exit tunnel. We further show that PF-06446846 reduces plasma PCSK9 and total cholesterol levels in rats following oral dosing. Using ribosome profiling, we demonstrate that PF-06446846 is highly selective for the inhibition of PCSK9 translation. The mechanism of action employed by PF-06446846 reveals a previously unexpected tunability of the human ribosome that allows small molecules to specifically block translation of individual transcripts.
Conflict of interest statement
NGL, DP, AL, DWP, LW, JX, MB, PML, BM, KFG, AH, KFM, RGD, and SL are employees of Pfizer, Inc.
Figures
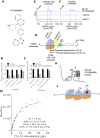
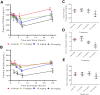
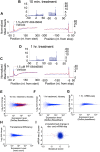
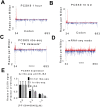
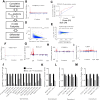
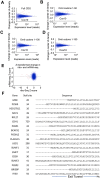
Comment in
-
Inhibiting Translation One Protein at a Time.Trends Biochem Sci. 2017 Jun;42(6):412-413. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 May 15. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017. PMID: 28522328
References
-
- Anderson KM, Castelli WP, Levy D. Cholesterol and mortality. 30 years of follow-up from the Framingham study. JAMA. 1987;257(16):2176–80. - PubMed
-
- Pearson TA, Blair SN, Daniels SR, Eckel RH, Fair JM, Fortmann SP, et al. AHA Guidelines for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease and Stroke: 2002 Update: Consensus Panel Guide to Comprehensive Risk Reduction for Adult Patients Without Coronary or Other Atherosclerotic Vascular Diseases. American Heart Association Science Advisory and Coordinating Committee. Circulation. 2002;106(3):388–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

