Insulin, IGF-1, and GH Receptors Are Altered in an Adipose Tissue Depot-Specific Manner in Male Mice With Modified GH Action
- PMID: 28323915
- PMCID: PMC5460824
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2017-00084
Insulin, IGF-1, and GH Receptors Are Altered in an Adipose Tissue Depot-Specific Manner in Male Mice With Modified GH Action
Abstract
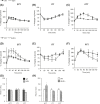
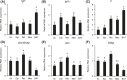
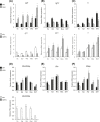
Growth hormone (GH) is a determinant of glucose homeostasis and adipose tissue (AT) function. Using 7-month-old transgenic mice expressing the bovine growth hormone (bGH) gene and growth hormone receptor knockout (GHR-/-) mice, we examined whether changes in GH action affect glucose, insulin, and pyruvate tolerance and AT expression of proteins involved in the interrelated signaling pathways of GH, insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and insulin. Furthermore, we searched for AT depot-specific differences in control mice. Glycated hemoglobin levels were reduced in bGH and GHR-/- mice, and bGH mice displayed impaired gluconeogenesis as judged by pyruvate tolerance testing. Serum IGF-1 was elevated by 90% in bGH mice, whereas IGF-1 and insulin were reduced by 97% and 61% in GHR-/- mice, respectively. Igf1 RNA was increased in subcutaneous, epididymal, retroperitoneal, and brown adipose tissue (BAT) depots in bGH mice (mean increase ± standard error of the mean in all five depots, 153% ± 27%) and decreased in all depots in GHR-/- mice (mean decrease, 62% ± 4%). IGF-1 receptor expression was decreased in all AT depots of bGH mice (mean decrease, 49% ± 6%) and increased in all AT depots of GHR-/- mice (mean increase, 94% ± 8%). Insulin receptor expression was reduced in retroperitoneal, mesenteric, and BAT depots in bGH mice (mean decrease in all depots, 56% ± 4%) and augmented in subcutaneous, retroperitoneal, mesenteric, and BAT depots in GHR-/- mice (mean increase: 51% ± 1%). Collectively, our findings indicate a role for GH in influencing hormone signaling in AT in a depot-dependent manner.
Copyright © 2017 Endocrine Society.
Figures



References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Després J-P, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Isasi CR, Jiménez MC, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Rosamond W, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB Heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update. A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133 (4):e38–e360. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association 6. Obesity management for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(Suppl 1):S47–S51. - PubMed
-
- Hjortebjerg R, Flyvbjerg A, Frystyk J. Insulin growth factor binding proteins as therapeutic targets in type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014;18(2):209–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

