Establishing cytogenetic biodosimetry laboratory in Saudi Arabia and producing preliminary calibration curve of dicentric chromosomes as biomarker for medical dose estimation in response to radiation emergencies
- PMID: 28324310
- PMCID: PMC4235882
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-014-0217-x
Establishing cytogenetic biodosimetry laboratory in Saudi Arabia and producing preliminary calibration curve of dicentric chromosomes as biomarker for medical dose estimation in response to radiation emergencies
Abstract
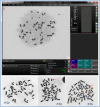
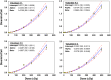
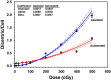
In cases of public or occupational radiation overexposure and eventual radiological accidents, it is important to provide dose assessment, medical triage, diagnoses and treatment to victims. Cytogenetic bio-dosimetry based on scoring of dicentric chromosomal aberrations assay (DCA) is the "gold standard" biotechnology technique for estimating medically relevant radiation doses. Under the auspices of the National Science, Technology and Innovation Plan in Saudi Arabia, we have set up a biodosimetry laboratory and produced a national standard dose-response calibration curve for DCA, pre-required to estimate the doses received. For this, the basic cytogenetic DCA technique needed to be established. Peripheral blood lymphocytes were collected from four healthy volunteers and irradiated with radiation doses between 0 and 5 Gy of 320 keV X-rays. Then, lymphocytes were PHA stimulated, Colcemid division arrested and stained cytogenetic slides were prepared. The Metafer4 system (MetaSystem) was used for automatic and manually assisted metaphase finding and scoring of dicentric chromosomes. Results were fit to the linear-quadratic dose-effect model according to the IAEA EPR-Biodosimetry-2011 report. The resulting manually assisted dose-response calibration curve (Y = 0.0017 + 0.026 × D + 0.081 × D2) was in the range of those described in other populations. Although the automated scoring over-and-under estimates DCA at low (<1 Gy) and high (>2 Gy) doses, respectively, it showed potential for use in triage mode to segregate between victims with potential risk to develop acute radiotoxicity syndromes. In conclusion, we have successfully established the first biodosimetry laboratory in the region and have produced a preliminary national dose-response calibration curve. The laboratory can now contribute to the national preparedness plan in response to eventual radiation emergencies in addition to providing information for decision makers and public health officials who assess the magnitude of public, medical, occupational and accidental radiation exposures.
Keywords: Biodosimetry; Cytogenetics; Dicentric chromosomes; Dose–response calibration curve; Radiation overexposure.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander GASH, Amundson SA, Blakely WF, Buddemeier B, Gallez B, Dainiak N, Goans RE, Hayes RB, Lowry PC, Noska MA, Okunieff P, Salner AL, Schauer DA, Trompier F, Turteltaub KW, Voisin P, Wiley AL, Jr, Wilkins R. BiodosEPR-2006 Meeting: acute dosimetry consensus committee recommendations on biodosimetry applications in events involving uses of radiation by terrorists and radiation accidents. Radiat Meas. 2007;42(6–7):24.
-
- Aljohani MS (2008) Peaceful applications of nuclear technology in the GCC countries. In: Atom for peace conferences, Jeddah
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

