Assessment of genetic diversity of Bacillus spp. isolated from eutrophic fish culture pond
- PMID: 28324539
- PMCID: PMC4522712
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-014-0234-9
Assessment of genetic diversity of Bacillus spp. isolated from eutrophic fish culture pond
Abstract
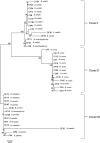
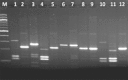
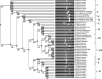
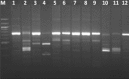
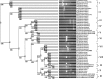
The genus Bacillus comprises of a diverse group with a wide range of nutritional requirements and physiological and metabolic diversity. Their role in nutrient cycle is well documented. 16S rDNA sequences do not always allow the species to be discriminated. In this study 40 Bacillus spp. obtained from fish culture pond and 10 culture type strains were analysed for their genomic diversity by PCR-RFLP of intergenic spacer region of 16S-23S and HSP60 genes. TaqI digestion of PCR products amplified by ITS PCR did not render distinctive RFLP patterns. Numerical analysis of ITS PCR-RFLP pattern differentiated the isolates into 11 clusters. Same species were found to be grouped in different clusters. But PstI digested PCR products amplified from HSP60 gene of the isolates showed distinctive RFLP patterns. The dendrogram constructed from HSP60 PCR-RFLP delineated the isolates into 11 clusters also. All the clusters, except cluster I grouped only one type of species. The results showed that Bacillus spp. could be clearly distinguished by PCR-RFLP of HSP60 gene. Therefore, the HSP60 gene is proposed as an additional molecular marker for discrimination of Bacillus group.
Keywords: Bacillus group; HSP60 gene; ITS; Molecular marker; PCR–RFLP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of acetic acid bacteria by RFLP of PCR-amplified 16S rDNA and 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000 Nov;50 Pt 6:1981-1987. doi: 10.1099/00207713-50-6-1981. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11155971
-
Differentiation of petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading Pseudomonas spp. based on PCR-RFLP of the 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer region.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2012 Jan;57(1):47-52. doi: 10.1007/s12223-011-0088-z. Epub 2011 Dec 23. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2012. PMID: 22193887
-
Restriction fragment length polymorphism of 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer of Aeromonas spp.Syst Appl Microbiol. 2004 Sep;27(5):549-57. doi: 10.1078/0723202041748226. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15490556
-
Genetic diversity of bradyrhizobial populations from diverse geographic origins that nodulate Lupinus spp. and Ornithopus spp.Syst Appl Microbiol. 2003 Nov;26(4):611-23. doi: 10.1078/072320203770865927. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14666990
-
Identification of Lactobacillus alimentarius and Lactobacillus farciminis with 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer region polymorphism and PCR amplification using species-specific oligonucleotide.J Appl Microbiol. 2003;95(6):1207-16. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2003.02117.x. J Appl Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14632993
Cited by
-
Assessment of the phenotypic and genotypic diversity of endophytic strains of Bacillus and closely related genera from Carpinus betulus in the Hyrcanian forests of Iran.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 16;51(1):306. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09221-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38363387
-
Deciphering the evolutionary affiliations among bacterial strains (Pseudomonas and Frankia sp.) inhabiting same ecological niche using virtual RFLP and simulation-based approaches.3 Biotech. 2016 Dec;6(2):178. doi: 10.1007/s13205-016-0488-5. Epub 2016 Aug 23. 3 Biotech. 2016. PMID: 28330250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ash C, Farrow JAE, Wallbanks S, Collins MD. Phylogenetic heterogeneity of the genus Bacillus as revealed by comparative analysis of small-subunit-ribosomal RNA sequences. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1991;13:202–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.1991.tb00608.x. - DOI
-
- Banik S, Ninawe A. Phosphate solubilising microorganism in water and sediments of a tropical estuary and the adjacent coastal Arabian Sea, in relation to their physic chemical properties. J Indian Soc Coast Agril Res. 1988;6:75–83.
-
- Chen YP, Rekha PD, Arun AB, Shen FT, Lai W-A, Young CC. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilising abilities. Appl Soil Ecol. 2006;34:33–41. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2005.12.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

