Lysophospholipids and Their Receptors Serve as Conditional DAMPs and DAMP Receptors in Tissue Oxidative and Inflammatory Injury
- PMID: 28325059
- PMCID: PMC5849278
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2017.7069
Lysophospholipids and Their Receptors Serve as Conditional DAMPs and DAMP Receptors in Tissue Oxidative and Inflammatory Injury
Abstract
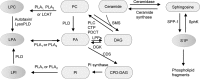
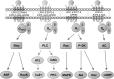
Significance: We proposed lysophospholipids (LPLs) and LPL-G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) as conditional danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and conditional DAMP receptors as a paradigm shift to the widely accepted classical DAMP and DAMP receptor model. Recent Advances: The aberrant levels of LPLs and GPCRs activate pro-inflammatory signal transduction pathways, trigger innate immune response, and lead to tissue oxidative and inflammatory injury. Critical Issues: Classical DAMP model specifies only the endogenous metabolites that are released from damaged/dying cells as DAMPs, but fails to identify elevated endogenous metabolites secreted from viable/live cells during pathologies as DAMPs. The current classification of DAMPs also fails to clarify the following concerns: (i) Are molecules, which bind to pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), the only DAMPs contributing to inflammation and tissue injury? (ii) Are all DAMPs acting only via classical PRRs during cellular stress? To answer these questions, we reviewed the molecular characteristics and signaling mechanisms of LPLs, a group of endogenous metabolites and their specific receptors and analyzed the significant progress achieved in characterizing oxidative stress mechanisms of LPL mediated tissue injury. Future Directions: Further LPLs and LPL-GPCRs may serve as potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of pathologies induced by sterile inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 28, 973-986.
Keywords: G-protein-coupled receptors; conditional danger-associated molecular patterns; inflammation; lysophospholipids; mitochondrial reactive oxygen species; oxidative stress.
Figures


References
-
- Aoki J, Taira A, Takanezawa Y, Kishi Y, Hama K, Kishimoto T, Mizuno K, Saku K, Taguchi R, and Arai H. Serum lysophosphatidic acid is produced through diverse phospholipase pathways. J Biol Chem 277: 48737–48744, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Bauernfeind FG, Horvath G, Stutz A, Alnemri ES, MacDonald K, Speert D, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, Monks BG, Fitzgerald KA, Hornung V, and Latz E. Cutting edge: NF-kappaB activating pattern recognition and cytokine receptors license NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating NLRP3 expression. J Immunol 183: 787–791, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

