Towards integrating extracellular matrix and immunological pathways
- PMID: 28325629
- PMCID: PMC5581707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.03.004
Towards integrating extracellular matrix and immunological pathways
Abstract
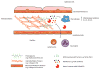
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a complex and dynamic structure made up of an estimated 300 different proteins. The ECM is also a rich source of cytokines and growth factors in addition to numerous bioactive ECM degradation products that influence cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation. The ECM is constantly being remodeled during homeostasis and in a wide range of pathological contexts. Changes in the ECM modulate immune responses, which in turn regulate repair and regeneration of tissues. Here, we review the many components of the ECM, enzymes involved in ECM remodeling, and the signals that feed into immunological pathways in the context of a dynamic ECM. We highlight studies that have taken an integrative approach to studying immune responses in the context of the ECM and studies that use novel proteomic strategies. Finally, we discuss research challenges relevant to the integration of immune and ECM networks and propose experimental and translational approaches to resolve these issues.
Keywords: Extracellular matrix; Immunology; Matrikines; Matrix metalloproteinases; Tissue remodeling.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Huxley-Jones J, Robertson DL, Boot-Handford RP. On the origins of the extracellular matrix in vertebrates. Matrix Biol. 2007 Jan;26(1):2–11. - PubMed
-
- Huxley-Jones J, Apte SS, Robertson DL, Boot-Handford RP. The characterisation of six ADAMTS proteases in the basal chordate Ciona intestinalis provides new insights into the vertebrate ADAMTS family. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Sep;37(9):1838–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

