Percutaneous Cryoablation for Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 28326265
- PMCID: PMC5345531
- DOI: 10.15586/jkcvhl.2015.34
Percutaneous Cryoablation for Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults. Nephron sparing resection (partial nephrectomy) has been the "gold standard" for the treatment of resectable disease. With the widespread use of cross sectional imaging techniques, more cases of renal cell cancers are detected at an early stage, i.e. stage 1A or 1B. This has provided an impetus for expanding the nephron sparing options and especially, percutaneous ablative techniques. Percutaneous ablation for RCC is now performed as a standard therapeutic nephron-sparing option in patients who are poor candidates for resection or when there is a need to preserve renal function due to comorbid conditions, multiple renal cell carcinomas, and/or heritable renal cancer syndromes. During the last few years, percutaneous cryoablation has been gaining acceptance as a curative treatment option for small renal cancers. Clinical studies to date indicate that cryoablation is a safe and effective therapeutic method with acceptable short and long term outcomes and with a low risk, in the appropriate setting. In addition it seems to offer some advantages over radio frequency ablation (RFA) and other thermal ablation techniques for renal masses.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Dr. Christos Georgaides is a Consultant for Galil Medical (Israel) and Endocare (USA).
Figures
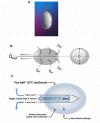
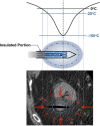
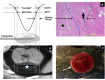

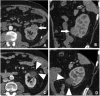
References
-
- Homma Y, Kawabe K, Kitamura T, Nishimura Y, Shinohara M, Kondo Y, Saito I, Minowada S, Asakage Y. Increased incidental detection and reduced mortality in renal cancer: recent retrospective analysis at eight institutions. Int J Urol. 1995;2(2):77–80. Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1442–2042.1995.tb00428.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fergany AF, Hafez KS, Novick AC. Long-term results of nephron sparing surgery for localized renal cell carcinoma: 10-year follow-up. J Urol. 2000;163(2):442–5. Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(05)67896-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Woldu SL, et al. Comparison of Renal Parenchymal Volume Preservation Between Partial Nephrectomy, Cryoablation, and Radiofrequency Ablation. epub ahead of print. J Endourol. March 2015 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/end.2014.0866. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Campbell SC, et al. Guidelines for management of the clinical T1 renal mass. J Urol. 2009;182(4):1271–9. Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.07.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kunkle DA, Uzzo RG. Cryoablation or radiofrequency ablation of the small renal mass: a meta-analysis. Cancer. 2008;113(10):2671–80. Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23896. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
