Ameliorating Effect of Gemigliptin on Renal Injury in Murine Adriamycin-Induced Nephropathy
- PMID: 28326327
- PMCID: PMC5343226
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/7275109
Ameliorating Effect of Gemigliptin on Renal Injury in Murine Adriamycin-Induced Nephropathy
Abstract
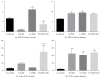
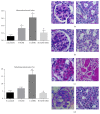
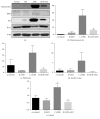
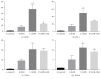
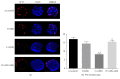
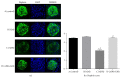
Background. Previous studies have shown the antiapoptotic and anti-inflammatory potential of DPP-IV inhibitor in experimental models of renal injury. We tested whether DPP-IV inhibitor (gemigliptin) ameliorates renal injury by suppressing apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in mice with adriamycin nephropathy. Methods. Mice were treated with normal saline (control), gemigliptin (GM), adriamycin (ADR), or adriamycin combined with gemigliptin (ADR+GM). Apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress were analyzed via western blotting, real-time PCR, light microscopy, and immunofluorescence. Results. In the ADR+GM group, urine albumin creatinine ratio decreased significantly compared with that in the ADR group on day 15. Glomerulosclerosis index and tubulointerstitial injury index in mice with adriamycin-induced nephropathy decreased after gemigliptin treatment. ADR group showed higher levels of apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress-related molecules compared with the control group. The upregulation of these molecules was significantly reduced by gemigliptin. In the ADR group, the staining intensities of WT-1 and nephrin reduced, but these changes were ameliorated in the ADR+GM group. Conclusion. We demonstrated that gemigliptin ameliorates nephropathy by suppressing apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in mice administered adriamycin. Our data demonstrate that gemigliptin has renoprotective effects on adriamycin-induced nephropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Tiruppathi C., Miyamoto Y., Ganapathy V., Roesel R. A., Whitford G. M., Leibach F. H. Hydrolysis and transport of proline-containing peptides in renal brush-border membrane vesicles from dipeptidyl peptidase IV-positive and dipeptidyl peptidase IV-negative rat strains. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1990;265(3):1476–1483. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

