Total knee arthroplasty in patients with extra-articular deformity
- PMID: 28326394
- PMCID: PMC4957157
- DOI: 10.1016/j.artd.2015.11.002
Total knee arthroplasty in patients with extra-articular deformity
Abstract
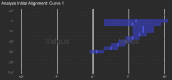
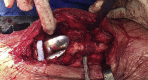
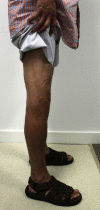
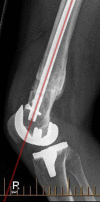
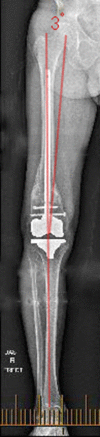
Multiple acceptable options are available for the correction of distal femoral deformity associated with knee arthritis. The treatment modality should be chosen based on the extent of deformity and attention to preservation of the collateral ligaments. Surgical options range from osteotomy alone, arthroplasty with intra-articular correction, or arthroplasty with extra-articular correction. Different implant choices and fixation methods for the osteotomy possess advantages and disadvantages which need to be considered carefully. In addition to discussing principles of management based on current literature, this article includes a case report using a previously undescribed technique using corrective osteotomy, intramedullary nail fixation, and total knee arthroplasty with computer navigation.
Keywords: Computer navigation; Corrective femoral osteotomy; Distal femoral deformity; Total knee arthroplasty.
Figures
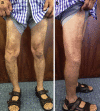
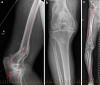
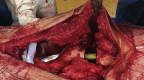
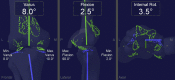









References
-
- Enninghorst N., McDougall D., Evans J.A., Sisak K., Balogh Z.J. Population-based epidemiology of femur shaft fractures. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;74(6):1516. - PubMed
-
- Ehlinger M., Ducrot G., Adam P., Bonnomet F. Distal femur fractures. Surgical techniques and a review of the literature. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(3):353. - PubMed
-
- Wolff A.M., Hungerford D.S., Pepe C.L. The effect of extraarticular varus and valgus deformity on total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(271):35. - PubMed
-
- Bansi P., Tetsworth K. Total-knee replacement for the management of periarticular knee fractures in the elderly. Curr Opin Orthop. 2006;17(1):51.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

