Role of dorsal root ganglion K2p1.1 in peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain
- PMID: 28326939
- PMCID: PMC5367768
- DOI: 10.1177/1744806917701135
Role of dorsal root ganglion K2p1.1 in peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain
Abstract
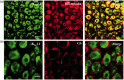
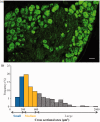
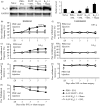
Peripheral nerve injury-caused hyperexcitability and abnormal ectopic discharges in the primary sensory neurons of dorsal root ganglion (DRG) play a key role in neuropathic pain development and maintenance. The two-pore domain background potassium (K2P) channels have been identified as key determinants of the resting membrane potential and neuronal excitability. However, whether K2P channels contribute to neuropathic pain is still elusive. We reported here that K2P1.1, the first identified mammalian K2P channel, was highly expressed in mouse DRG and distributed in small-, medium-, and large-sized DRG neurons. Unilateral lumbar (L) 4 spinal nerve ligation led to a significant and time-dependent reduction of K2P1.1 mRNA and protein in the ipsilateral L4 DRG, but not in the contralateral L4 or ipsilateral L3 DRG. Rescuing this reduction through microinjection of adeno-associated virus-DJ expressing full-length K2P1.1 mRNA into the ipsilateral L4 DRG blocked spinal nerve ligation-induced mechanical, thermal, and cold pain hypersensitivities during the development and maintenance periods. This DRG viral microinjection did not affect acute pain and locomotor function. Our findings suggest that K2P1.1 participates in neuropathic pain development and maintenance and may be a potential target in the management of this disorder.
Figures




Similar articles
-
TET1 overexpression attenuates paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain through rescuing K2p1.1 expression in primary sensory neurons of male rats.Life Sci. 2022 May 15;297:120486. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120486. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35304127 Free PMC article.
-
FUS Contributes to Nerve Injury-Induced Nociceptive Hypersensitivity by Activating NF-κB Pathway in Primary Sensory Neurons.J Neurosci. 2023 Feb 15;43(7):1267-1278. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2082-22.2022. Epub 2023 Jan 10. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36627209 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels in adjacent intact L4 dorsal root ganglion neurons in neuropathic pain rats with L5 spinal nerve ligation.Neurosci Res. 2019 May;142:30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2018.04.002. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Neurosci Res. 2019. PMID: 29684385
-
Recent evidence for activity-dependent initiation of sympathetic sprouting and neuropathic pain.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008 Oct 25;60(5):617-27. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18958370 Review.
-
Are voltage-gated sodium channels on the dorsal root ganglion involved in the development of neuropathic pain?Mol Pain. 2011 Feb 23;7:16. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-16. Mol Pain. 2011. PMID: 21345196 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drug distribution in dorsal root ganglion after peripheral application of Lidocaine patch.Sci Rep. 2025 May 15;15(1):16913. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01169-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40374657 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Methylation: A Target in Neuropathic Pain.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 7;9:879902. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.879902. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35872752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic modifications in neuropathic pain.Mol Pain. 2021 Jan-Dec;17:17448069211056767. doi: 10.1177/17448069211056767. Mol Pain. 2021. PMID: 34823400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TET1 overexpression attenuates paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain through rescuing K2p1.1 expression in primary sensory neurons of male rats.Life Sci. 2022 May 15;297:120486. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120486. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35304127 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of TRPC6 Mediated by PAX6 Hypomethylation Is Involved in the Mechanical Allodynia Induced by Chemotherapeutics in Dorsal Root Ganglion.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020 Apr 23;23(4):257-267. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa014. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32124922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chung JM, Chung K. Importance of hyperexcitability of DRG neurons in neuropathic pain. Pain Pract 2002; 2: 87–97. - PubMed
-
- Devor M. Ectopic discharge in Abeta afferents as a source of neuropathic pain. Exp Brain Res 2009; 196: 115–128. - PubMed
-
- Kindler CH, Yost CS. Two-pore domain potassium channels: new sites of local anesthetic action and toxicity. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2005; 30: 260–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

