metaX: a flexible and comprehensive software for processing metabolomics data
- PMID: 28327092
- PMCID: PMC5361702
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-017-1579-y
metaX: a flexible and comprehensive software for processing metabolomics data
Abstract
Background: Non-targeted metabolomics based on mass spectrometry enables high-throughput profiling of the metabolites in a biological sample. The large amount of data generated from mass spectrometry requires intensive computational processing for annotation of mass spectra and identification of metabolites. Computational analysis tools that are fully integrated with multiple functions and are easily operated by users who lack extensive knowledge in programing are needed in this research field.
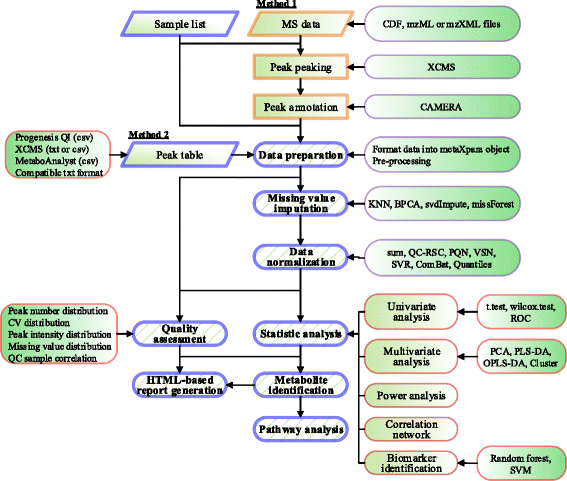
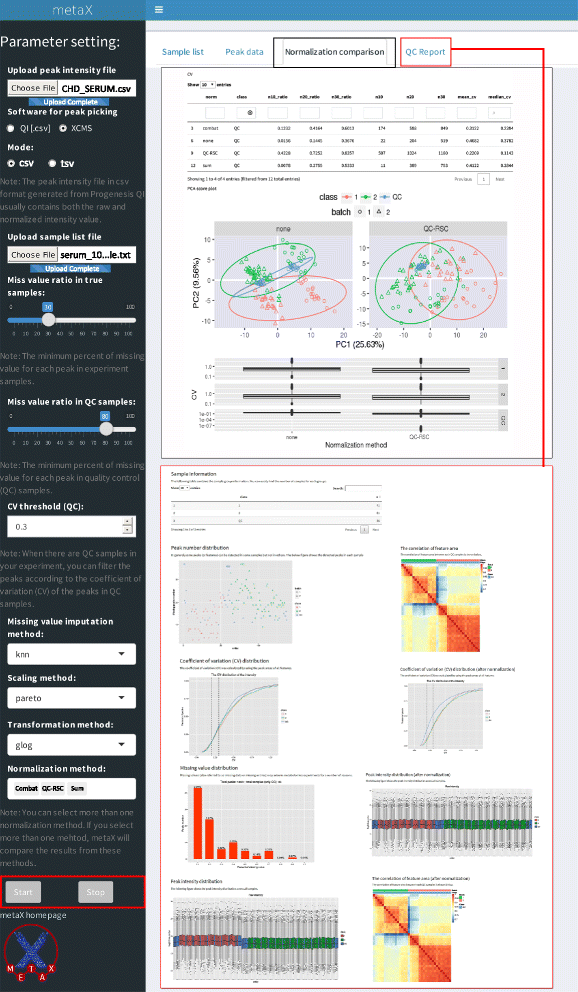
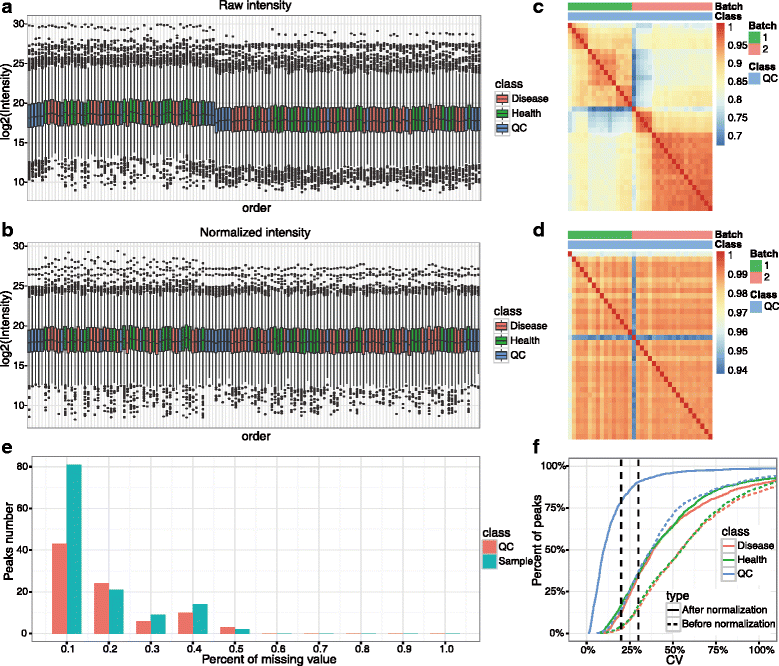
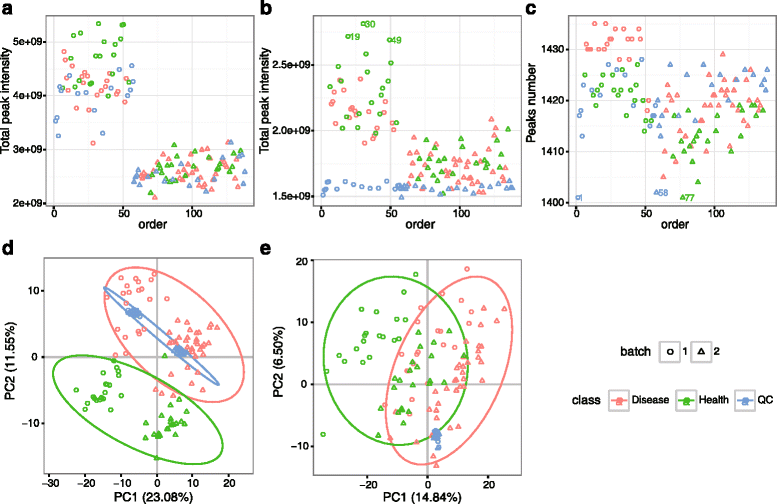
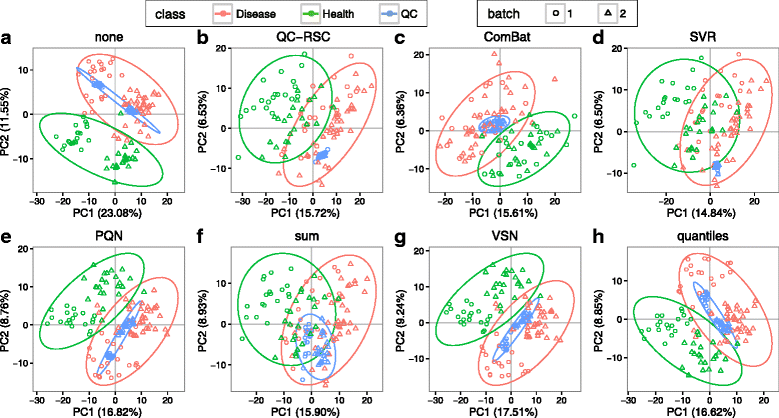
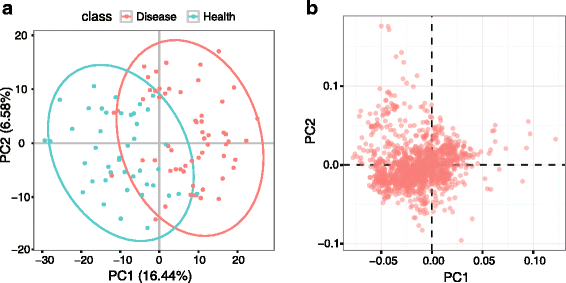
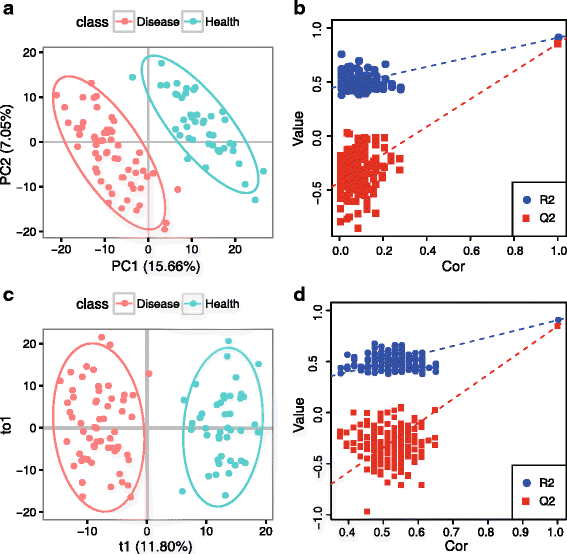
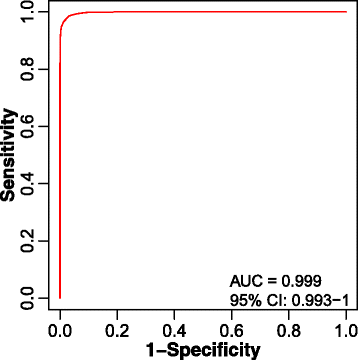
Results: We herein developed an R package, metaX, that is capable of end-to-end metabolomics data analysis through a set of interchangeable modules. Specifically, metaX provides several functions, such as peak picking and annotation, data quality assessment, missing value imputation, data normalization, univariate and multivariate statistics, power analysis and sample size estimation, receiver operating characteristic analysis, biomarker selection, pathway annotation, correlation network analysis, and metabolite identification. In addition, metaX offers a web-based interface ( http://metax.genomics.cn ) for data quality assessment and normalization method evaluation, and it generates an HTML-based report with a visualized interface. The metaX utilities were demonstrated with a published metabolomics dataset on a large scale. The software is available for operation as either a web-based graphical user interface (GUI) or in the form of command line functions. The package and the example reports are available at http://metax.genomics.cn/ .
Conclusions: The pipeline of metaX is platform-independent and is easy to use for analysis of metabolomics data generated from mass spectrometry.
Keywords: Metabolomics; Normalization; Pipeline; Quality control; Workflow.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

