Rumination mediates the relationship between overgeneral autobiographical memory and depression in patients with major depressive disorder
- PMID: 28327097
- PMCID: PMC5361774
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-017-1264-8
Rumination mediates the relationship between overgeneral autobiographical memory and depression in patients with major depressive disorder
Abstract
Background: Overgeneral autobiographical memory has been identified as a risk factor for the onset and maintenance of depression. However, little is known about the underlying mechanisms that might explain overgeneral autobiographical memory phenomenon in depression. The purpose of this study was to test the mediation effects of rumination on the relationship between overgeneral autobiographical memory and depressive symptoms. Specifically, the mediation effects of brooding and reflection subtypes of rumination were examined in patients with major depressive disorder.
Methods: Eighty-seven patients with major depressive disorder completed the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, Ruminative Response Scale, and Autobiographical Memory Test. Bootstrap mediation analysis for simple and multiple mediation models through the PROCESS macro was applied.
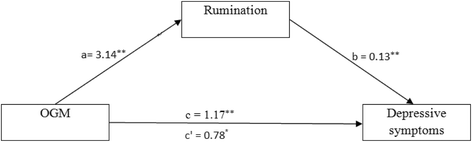
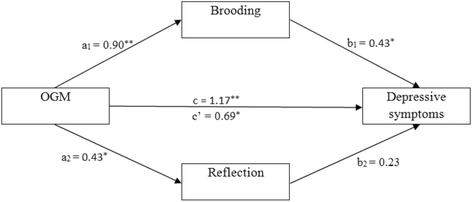
Results: Simple mediation analysis showed that rumination significantly mediated the relationship between overgeneral autobiographical memory and depression symptoms. Multiple mediation analyses showed that brooding, but not reflection, significantly mediated the relationship between overgeneral autobiographical memory and depression symptoms.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that global rumination partly mediates the relationship between overgeneral autobiographical memory and depressive symptoms in patients with major depressive disorder. Furthermore, the present results suggest that the mediating role of rumination in the relationship between overgeneral autobiographical memory and depression is mainly due to the maladaptive brooding subtype of rumination.
Keywords: Depressive symptoms; Mediation analysis; Overgeneral autobiographical memory; Rumination.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

