Deterministic secure quantum communication using a single d-level system
- PMID: 28327557
- PMCID: PMC5361180
- DOI: 10.1038/srep44934
Deterministic secure quantum communication using a single d-level system
Abstract
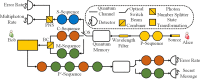
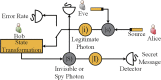
Deterministic secure quantum communication (DSQC) can transmit secret messages between two parties without first generating a shared secret key. Compared with quantum key distribution (QKD), DSQC avoids the waste of qubits arising from basis reconciliation and thus reaches higher efficiency. In this paper, based on data block transmission and order rearrangement technologies, we propose a DSQC protocol. It utilizes a set of single d-level systems as message carriers, which are used to directly encode the secret message in one communication process. Theoretical analysis shows that these employed technologies guarantee the security, and the use of a higher dimensional quantum system makes our protocol achieve higher security and efficiency. Since only quantum memory is required for implementation, our protocol is feasible with current technologies. Furthermore, Trojan horse attack (THA) is taken into account in our protocol. We give a THA model and show that THA significantly increases the multi-photon rate and can thus be detected.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
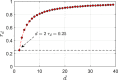
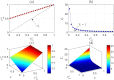
 versus the original multi-photon rate
versus the original multi-photon rate  . (b) Increase rate Ir of multi-photon rate versus
. (b) Increase rate Ir of multi-photon rate versus  . (c) In the case that Eve inserts a spy photon in a signal with probability s,
. (c) In the case that Eve inserts a spy photon in a signal with probability s,  versus
versus  and s. (d) Increase rate Ir of multi-photon rate versus
and s. (d) Increase rate Ir of multi-photon rate versus  and s.
and s.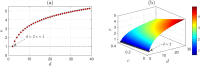
Similar articles
-
Deterministic Secure Quantum Communication on the BB84 System.Entropy (Basel). 2020 Nov 7;22(11):1268. doi: 10.3390/e22111268. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33287036 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled bidirectional quantum secure direct communication.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:694798. doi: 10.1155/2014/694798. Epub 2014 May 5. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 25006596 Free PMC article.
-
Provably Secure Symmetric Private Information Retrieval with Quantum Cryptography.Entropy (Basel). 2020 Dec 31;23(1):54. doi: 10.3390/e23010054. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33396236 Free PMC article.
-
Quantum communication with coherent states of light.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2017 Aug 6;375(2099):20160235. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2016.0235. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2017. PMID: 28652491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Geometrical Optics Restricted Quantum Key Distribution.Entropy (Basel). 2021 Jul 31;23(8):1003. doi: 10.3390/e23081003. Entropy (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34441143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deterministic Secure Quantum Communication on the BB84 System.Entropy (Basel). 2020 Nov 7;22(11):1268. doi: 10.3390/e22111268. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33287036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennett C. H. & Brassard G. Quantum cryptography: punlic key distribution and coin tossing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, 175 (1984).
-
- Gisin N., Ribordy G., Tittel W. & Zbinden H. Qunatum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145 (2002).
-
- Long G. L. & Liu X. S. Theoretical efficient high capacity quantum key distribution scheme. arXiv:quantph/0012056 (2000).
-
- Beige A., Englert B. G., Kurtsiefer C. & Weinfurter H. Secure communication with a publicly known key. Phys. Pol. A 101, 357 (2002).
-
- Li X. H., Deng F. G. & Zhou H. Y. Improving the security of secure direct communication based on the secret transmitting order of particles. Phys. Rev. A 74, 054302 (2006).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

