The role of genetic counsellors in genomic healthcare in the United Kingdom: a statement by the Association of Genetic Nurses and Counsellors
- PMID: 28327572
- PMCID: PMC5518913
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2017.28
The role of genetic counsellors in genomic healthcare in the United Kingdom: a statement by the Association of Genetic Nurses and Counsellors
Abstract
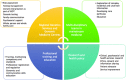
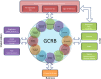
In the United Kingdom, genetic counsellors work together with clinical geneticists and clinical scientist colleagues within specialist genetics services, but they also often work in multidisciplinary teams (MDTs) outside of such services. There, they contribute genetic knowledge together with expert understanding of how to communicate genetic information effectively. They can offer education and support to the MDT, while providing management advice for both affected patients and the extended at-risk family members. As genomic technologies are implemented across many disciplines within healthcare, genetic counsellors are playing a key role in enabling non-genetic health professionals learn, understand and integrate genomic data into their practice. They are also involved in curriculum development, workforce planning, research, regulation and policy creation - all with the aim of ensuring a robust evidence base from which to practise, together with clear guidelines on what constitutes competence and good practice. The Association of Genetic Nurses and Counsellors (AGNC) in The United Kingdom (UK) and Republic of Ireland is committed to supporting genetic counsellors, across all sectors of healthcare and research, as they help deliver genomic medicine for the patient, family and world-class health services.European Journal of Human Genetics advance online publication, 22 March 2017; doi:10.1038/ejhg.2017.28.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- AGNC. Association of Genetic Nurses and Counsellors Vision Statement: The future role of Genetic Counsellors in Genomic Healthcare, 2017; last updated: 5 March 2015. Accessed on 9 Januar17; Available at http://www.agnc.org.uk/media/925792/agnc_vision_statement_final.pdf.
-
- Human Genomics Strategy Group. Building on our inheritance: genomic technology in healthcare. 2012; Publication from the Department of Health. Available at https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/fil....
-
- Burton H: Genetics and Mainstream Medicine. PHG Foundation, Cambridge, UK, 2011. ISBN 978-1-907198-07-6.
-
- Paneque M, Molvan R, Cordier C et al: Genetic Counselling Profession in Europe: in eLS. John Wiley and Sons Ltd, Chichester, UK, 2016.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials