Hypoxia induces H19 expression through direct and indirect Hif-1α activity, promoting oncogenic effects in glioblastoma
- PMID: 28327666
- PMCID: PMC5361208
- DOI: 10.1038/srep45029
Hypoxia induces H19 expression through direct and indirect Hif-1α activity, promoting oncogenic effects in glioblastoma
Abstract
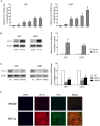
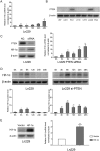
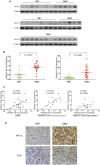
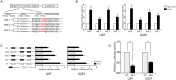
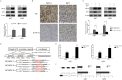
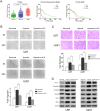
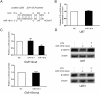
H19 expression is elevated in many human tumors including glioblastomas, suggesting an oncogenic role for the long noncoding RNA; yet the upregulation of H19 in glioblastomas remains unclear. Here we report that hypoxia significantly stimulated H19 expression in glioblastoma cell lines, which was related to hypoxia-inducible factors 1α (Hif-1α). Hif-1α promoted H19 expression in U87 and U251 cells. Meanwhile PTEN is an advantageous factor to affect H19 expression, through attenuating Hif-1α stability. Hif-1α also positively correlates with H19 in human glioblastoma samples depending on PTEN status. ChIP and luciferase reporter assays showed that Hif-1α induced H19 transcription through directly binding to the H19 promoter. Furthermore, Hif-1α upregulated specific protein 1 (SP1) expression in glioblastomas cells in vitro and in vivo, and SP1 also strongly interacted with the H19 promoter to promote H19 expression under hypoxia. We also showed that H19 acts as a molecular sponge that binds miR-181d, relieving inhibition of β-catenin expression. Therefore, H19 participates in hypoxia-driven migration and invasion in glioblastoma cells. In summary, our results uncover the mechanisms that stimulate H19 expression under hypoxia to promote malignant effects in glioblastomas and suggest H19 might be a promising therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Jensen R. L. Hypoxia in the tumorigenesis of gliomas and as a potential target for therapeutic measures. Neurosurg Focus 20, E24 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Evans S. M. et al. Hypoxia is important in the biology and aggression of human glial brain tumors. Clin Cancer Res 10, 8177–84 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Li S., Meng W., Guan Z., Guo Y. & Han X. The hypoxia-related signaling pathways of vasculogenic mimicry in tumor treatment. Biomed Pharmacother 80, 127–35 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Thambi T., Park J. H. & Lee D. S. Hypoxia-responsive nanocarriers for cancer imaging and therapy: recent approaches and future perspectives. Chem Commun (Camb) 52, 8492–500 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

