BTK inhibition is a potent approach to block IgE-mediated histamine release in human basophils
- PMID: 28328081
- PMCID: PMC5655929
- DOI: 10.1111/all.13166
BTK inhibition is a potent approach to block IgE-mediated histamine release in human basophils
Abstract
Background: Recent data suggest that Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is an emerging therapeutic target in IgE receptor (IgER)-cross-linked basophils.
Methods: We examined the effects of four BTK inhibitors (ibrutinib, dasatinib, AVL-292, and CNX-774) on IgE-dependent activation and histamine release in blood basophils obtained from allergic patients (n=11) and nonallergic donors (n=5). In addition, we examined the effects of these drugs on the growth of the human basophil cell line KU812 and the human mast cell line HMC-1.
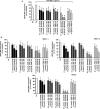
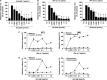
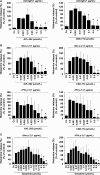
Results: All four BTK blockers were found to inhibit anti-IgE-induced histamine release from basophils in nonallergic subjects and allergen-induced histamine liberation from basophils in allergic donors. Drug effects on allergen-induced histamine release were dose dependent, with IC50 values ranging between 0.001 and 0.5 μmol/L, and the following rank order of potency: ibrutinib>AVL-292>dasatinib>CNX-774. The basophil-targeting effect of ibrutinib was confirmed by demonstrating that IgE-dependent histamine release in ex vivo blood basophils is largely suppressed in a leukemia patient treated with ibrutinib. Dasatinib and ibrutinib were also found to counteract anti-IgE-induced and allergen-induced upregulation of CD13, CD63, CD164, and CD203c on basophils, whereas AVL-292 and CNX-774 showed no significant effects. Whereas dasatinib and CNX-774 were found to inhibit the growth of HMC-1 cells and KU812 cells, no substantial effects were seen with ibrutinib or AVL-292.
Conclusions: BTK-targeting drugs are potent inhibitors of IgE-dependent histamine release in human basophils. The clinical value of BTK inhibition in the context of allergic diseases remains to be determined.
Keywords: IgE receptor; allergy; signaling molecules; targeted drugs.
© 2017 The Authors. Allergy Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Valent P, Bettelheim P. Cell surface structures on human basophils and mast cells: biochemical and functional characterization. Adv Immunol. 1992;52:333‐423. - PubMed
-
- Falcone FH, Haas H, Gibbs BF. The human basophil: a new appreciation of its role in immune responses. Blood. 2000;96:4028‐4038. - PubMed
-
- Kinet JP. The high‐affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI): from physiology to pathology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:931‐972. - PubMed
-
- Nadler MJ, Matthews SA, Turner H, Kinet JP. Signal transduction by the high‐affinity immunoglobulin E receptor Fc epsilon RI: coupling form to function. Adv Immunol. 2000;76:325‐355. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

