Pregnancy at Advanced Maternal Age Affects Behavior and Hippocampal Gene Expression in Mouse Offspring
- PMID: 28329103
- PMCID: PMC5861961
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glx016
Pregnancy at Advanced Maternal Age Affects Behavior and Hippocampal Gene Expression in Mouse Offspring
Abstract
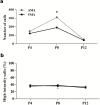
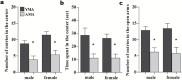
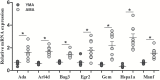
There is growing evidence that advanced maternal age is a risk factor for neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders in offspring. However, it remains unclear whether the altered brain programming induced by advanced maternal age is mediated by pre- or postnatal factors. Here, a mouse model was used to investigate whether pregnancy at advanced age may provoke behavioral and brain gene expression changes in offspring. Swiss Albino mice conceived by 3-month-old males and either 15-18-month-old (n = 11) or 3-month-old control females (n = 5), were delivered by cesarean section, fostered after birth by 3-month-old dams and subjected to a battery of behavioral tests. Furthermore, genome-wide mRNA expression was analyzed in the hippocampi of 4-month-old males offspring using microarrays. Offspring conceived by old mothers exhibited increased ultrasound vocalization activity during separation from the foster mother, increased anxiety-like behaviors in adult life, and altered patterns of hippocampal gene expression, compared to controls. These effects were not reversed by the postnatal maternal care provided by the young foster mothers, suggesting that the altered brain programming is already established at birth, consistent with prenatal effects related to maternal aging.
Keywords: Brain disorders; Delayed motherhood; Maternal effects.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Gerontological Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Hamilton BE, Martin JA, Osterman MJ, Curtain SC. Births: preliminary data for 2014. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2015;64:1–19. doi:10.13140/RG.2.1.2768.4000 - PubMed
-
- Oliveira M. The Reproductive Health Report: the state of sexual and reproductive health within the European Union 2007/2010–final report. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2011;16:1–70. doi:10.3109/13625187.2011.607690 - PubMed
-
- Joseph KS, Allen AC, Dodds L, Turner LA, Scott H, Liston R. The perinatal effects of delayed childbearing. Obstet Gynecol. 2005;105:1410–1418. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000163256.83313.36 - PubMed
-
- Cleary-Goldman J, Malone FD, Vidaver J, et al. ; FASTER Consortium. Impact of maternal age on obstetric outcome. Obstet Gynecol. 2005;105(5 Pt 1):983–990. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000158118.75532.51 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

