Re-evaluating the roles of myosin 18Aα and F-actin in determining Golgi morphology
- PMID: 28329908
- PMCID: PMC8579491
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.21364
Re-evaluating the roles of myosin 18Aα and F-actin in determining Golgi morphology
Abstract
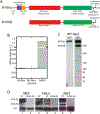
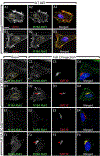
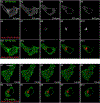
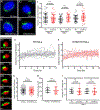
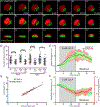
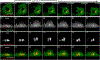
The peri-centrosomal localization and morphology of the Golgi apparatus depends largely on the microtubule cytoskeleton and the microtubule motor protein dynein. Recent studies proposed that myosin 18Aα (M18Aα) also contributes to Golgi morphology by binding the Golgi protein GOLPH3 and walking along adjacent actin filaments to stretch the Golgi into its classic ribbon structure. Biochemical analyses have shown, however, that M18A is not an actin-activated ATPase and lacks motor activity. Our goal, therefore, was to define the precise molecular mechanism by which M18Aα determines Golgi morphology. We show that purified M18Aα remains inactive in the presence of GOLPH3, arguing against the Golgi-specific activation of the myosin. Using M18A-specific antibodies and expression of GFP-tagged M18Aα, we find no evidence that it localizes to the Golgi. Moreover, several cell lines with reduced or eliminated M18Aα expression exhibited normal Golgi morphology. Interestingly, actin filament disassembly resulted in a marked reduction in lateral stretching of the Golgi in both control and M18Aα-deficient cells. Importantly, this reduction was accompanied by an expansion of the Golgi in the vertical direction, vertical movement of the centrosome, and increases in the height of both the nucleus and the cell. Collectively, our data indicate that M18Aα does not localize to the Golgi or play a significant role in determining its morphology, and suggest that global F-actin disassembly alters Golgi morphology indirectly by altering cell shape.
Keywords: Golgi; actin; microtubule organizing center; myosin 18A.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Cao H, Weller S, Orth JD, Chen J, Huang B, Chen JL, … McNiven MA (2005). Actin and Arf1-dependent recruitment of a cortactin-dynamin complex to the Golgi regulates post-Golgi transport. Nature Cell Biology, 7, 483–492. - PubMed
-
- Chen JL, Lacomis L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, & Stamnes M (2004). Cytosol-derived proteins are sufficient for Arp2/3 recruitment and ARF/coatomer-dependent actin polymerization on Golgi membranes. FEBS Letters, 566, 281–286. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

