Molecular characterization and amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis of entomopathogenic bacteria associated with Rhabditis (Oscheius) spp
- PMID: 28330100
- PMCID: PMC4713396
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-015-0326-1
Molecular characterization and amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis of entomopathogenic bacteria associated with Rhabditis (Oscheius) spp
Abstract
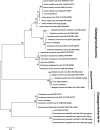
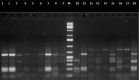
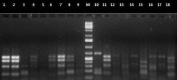
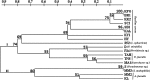
Bacterial strains associated with entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs) Rhabditis (Oscheius) spp. were isolated from infected cadavers of Galleria mellonella. The obtained 18 isolates were subdivided into nine phylogenetically different genera based on comparative sequence analysis of their 16S rRNA genes. The isolates were affiliated to three different class namely γ-proteobacteria (Enterobacter, Proteus, Providencia, Pseudomonas, Stenotrophomonas), β-proteobacteria (Alcaligenes) and Bacilli (Bacillus, Enterococcus, Lysinibacillus). It was observed that Gram-positive strains (Bacilli) were more frequently associated with the EPN, whereas Gram-negative isolates were affiliated to six different genera with more genotypic diversity. Subsequently, all bacterial isolates used in this study were analyzed by amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis (ARDRA). Eight restriction endonucleases (CfoI, HinfI, RsaI, DdeI, Sau3AI, AluI, HaeIII, and MspI) were examined and a total of 15 different genotypes were obtained, forming two heterogenous main clusters after analysis by un-weighted pair-group method using arithmetic averages.
Keywords: 16S rDNA; Bacillus; Enterobacter; Entomopathogenic nematode.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Figures

References
-
- Akhurst RJ (1996) From then to now—a brief review of entomopathogenic nematodes and their symbiotic bacteria. In: Second international symposium on entomopathogenic nematodes and their symbiotic bacteria, pp 3–8
-
- Akhurst RJ, Boemare NE. Biology and taxonomy of Xenorhabdus. In: Gaugler R, Kaya H, editors. Entomopathogenic nematodes in biological control. Boca Raton: CRC Press Inc; 1990. pp. 75–90.
-
- Boemare NE, Akhurst RJ. Biochemical and physiological characterization of colony form variants in Xenorhabdus spp. (Enterobacteriaceae) J Gen Microbiol. 1988;134:751–761. - PubMed
-
- Boemare NE, Akhurst RJ, Mourant RG. DNA relatedness between Xenorhabdus spp. (Enterobacteriaceae), symbiotic bacteria of entomopathogenic nematodes, and a proposal to transfer Xenorhabdus luminescens to a new genus, Photorhabdus gen. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 1993;43:249–255.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

