Novel pathway of cypermethrin biodegradation in a Bacillus sp. strain SG2 isolated from cypermethrin-contaminated agriculture field
- PMID: 28330116
- PMCID: PMC4742419
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-016-0372-3
Novel pathway of cypermethrin biodegradation in a Bacillus sp. strain SG2 isolated from cypermethrin-contaminated agriculture field
Abstract
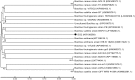
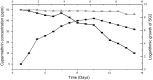
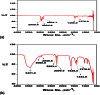
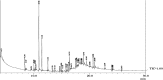
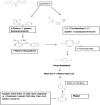
Pesticides belonging to pyrethroid group are widely used in agricultural fields to check pest infestation in different crops for enhanced food production. In spite of beneficial effects, non-judicious use of pesticides imposes harmful effect on human health as their residues reach different food materials and ground water via leaching, percolation and bioaccumulation. Looking into the potential of microbial degradation of toxic compounds under natural environment, a cypermethrin-degrading Bacillus sp. was isolated from pesticide-contaminated soil of a rice field of Distt. Udham Singh Nagar, Uttarakhand, India. The bacteria degraded the compound up to 81.6 % within 15 days under standard growth conditions (temperature 32 °C pH 7 and shaking at 116 rpm) in minimal medium. Analysis of intermediate compounds of biodegraded cypermethrin revealed that the bacteria opted a new pathway for cypermethrin degradation. GC-MS analysis of biodegraded cypermethrin showed the presence of 4-propylbenzoate, 4-propylbenzaldehyde, phenol M-tert-butyl and 1-dodecanol, etc. which was not reported earlier in cypermethrin metabolism; hence a novel biodegradation pathway of cypermethrin with Bacillus sp. strain SG2 is proposed in this study.
Keywords: Bacillus sp.; Biodegradation; Cypermethrin; GC–MS; Pyrethroid.
Conflict of interest statement
Author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anastassiades M, Lehotay SJ, Stajnbaher D, Schenck FJ. Fast and easy multi residue method employing extraction/partitioning and dispersive solid phase extraction for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J AOAC Int. 2003;86:412–431. - PubMed
-
- Bazzicalupo M, Fani R. The use of RAPD for generating specific DNA probes for microorganisms. In: Clap JP, editor. Methods in molecular biology. Species diagnostic protocols: PCR and other nucleic acid methods. Totowa: Humana Press Inc; 1995. pp. 155–175. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

