Predictors of hospital and one-year mortality in intensive care patients with refractory status epilepticus: a population-based study
- PMID: 28330483
- PMCID: PMC5363025
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1661-x
Predictors of hospital and one-year mortality in intensive care patients with refractory status epilepticus: a population-based study
Abstract
Background: The aim was to determine predictors of hospital and 1-year mortality in patients with intensive care unit (ICU)-treated refractory status epilepticus (RSE) in a population-based study.
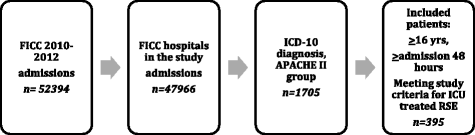
Methods: This was a retrospective study of the Finnish Intensive Care Consortium (FICC) database of adult patients (16 years of age or older) with ICU-treated RSE in Finland during a 3-year period (2010-2012). The database consists of admissions to all 20 Finnish hospitals treating RSE in the ICU. All five university hospitals and 11 out of 15 central hospitals participated in the present study. The total adult referral population in the study hospitals was 3.92 million, representing 91% of the adult population of Finland. Patients whose condition had a post-anoxic aetiological basis were excluded.
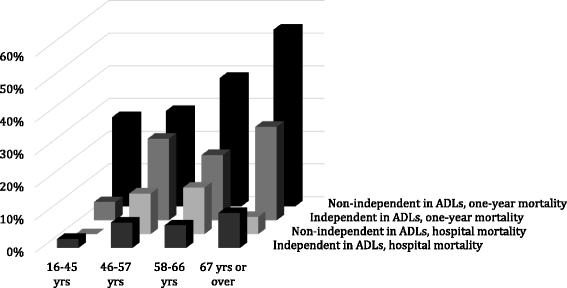
Results: We identified 395 patients with ICU-treated RSE, corresponding to an annual incidence of 3.4/100,000 (95% confidence interval (CI) 3.04-3.71). Hospital mortality was 7.4% (95% CI 0-16.9%), and 1-year mortality was 25.4% (95% CI 21.2-29.8%). Mortality at hospital discharge was associated with severity of organ dysfunction. Mortality at 1 year was associated with older age (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) 1.033, 95% CI 1.104-1.051, p = 0.001), sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score (aOR 1.156, CI 1.051-1.271, p = 0.003), super-refractory status epilepticus (SRSE) (aOR 2.215, 95% CI 1.20-3.84, p = 0.010) and dependence in activities of daily living (ADL) (aOR 2.553, 95% CI 1.537-4.243, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Despite low hospital mortality, 25% of ICU-treated RSE patients die within a year. Super-refractoriness, dependence in ADL functions, severity of organ dysfunction at ICU admission and older age predict long-term mortality.
Trial registration: Retrospective registry study; no interventions on human participants.
Keywords: ICU treatment; Incidence; Mortality; Outcome; Refractory status epilepticus; Status epilepticus; Super-refractory status epilepticus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence and mortality of super-refractory status epilepticus in adults.Epilepsy Behav. 2015 Aug;49:131-4. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.04.065. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Epilepsy Behav. 2015. PMID: 26141934
-
Long-term outcome of refractory status epilepticus in adults: A retrospective population-based study.Epilepsy Res. 2017 Jul;133:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2017.03.009. Epub 2017 Apr 2. Epilepsy Res. 2017. PMID: 28402834
-
Incidence of the different stages of status epilepticus in Eastern Finland: A population-based study.Epilepsy Behav. 2019 Dec;101(Pt B):106413. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.07.014. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Epilepsy Behav. 2019. PMID: 31371204
-
Efficacy and safety of perampanel in refractory and super-refractory status epilepticus: cohort study of 81 patients and literature review.J Neurol. 2021 Oct;268(10):3744-3757. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10506-9. Epub 2021 Mar 22. J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33754209 Review.
-
Pediatric refractory and super-refractory status epilepticus.Seizure. 2019 May;68:62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2018.05.012. Epub 2018 May 19. Seizure. 2019. PMID: 29941225 Review.
Cited by
-
Outcomes and Treatment Approaches for Super-Refractory Status Epilepticus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JAMA Neurol. 2023 Jul 31;80(9):959-68. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.2407. Online ahead of print. JAMA Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37523161 Free PMC article.
-
Postictal Encephalopathy After Status Epilepticus: Outcome and Risk Factors.Neurocrit Care. 2024 Jun;40(3):1025-1035. doi: 10.1007/s12028-023-01868-1. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Neurocrit Care. 2024. PMID: 37940836 Free PMC article.
-
Specific profiles of new-onset vs. non-inaugural status epilepticus: From diagnosis to 1-year outcome.Front Neurol. 2023 Feb 3;14:1101370. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1101370. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36860570 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes of status epilepticus: A critical assessment.Epilepsia. 2018 Oct;59 Suppl 2(Suppl Suppl 2):155-169. doi: 10.1111/epi.14515. Epub 2018 Aug 26. Epilepsia. 2018. PMID: 30146786 Free PMC article.
-
[Management of refractory and super-refractory status epilepticus].Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2019 Oct;114(7):628-634. doi: 10.1007/s00063-019-00610-0. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2019. PMID: 31463678 Review. German.
References
-
- Trinka E, Kalviainen R. 25 Years of advances in definition, classification and treatment of status epilepticus. England; Elsevier Ltd; 2017. Seizure. 44, pp. 65–73. British Epilepsy Association. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

