Reticular dysgenesis: international survey on clinical presentation, transplantation, and outcome
- PMID: 28331055
- PMCID: PMC5445572
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-11-745638
Reticular dysgenesis: international survey on clinical presentation, transplantation, and outcome
Abstract
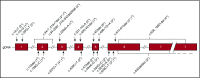
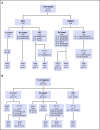
Reticular dysgenesis (RD) is a rare congenital disorder defined clinically by the combination of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), agranulocytosis, and sensorineural deafness. Mutations in the gene encoding adenylate kinase 2 were identified to cause the disorder. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the only option to cure this otherwise fatal disease. Retrospective data on clinical presentation, genetics, and outcome of HSCT were collected from centers in Europe, Asia, and North America for a total of 32 patients born between 1982 and 2011. Age at presentation was <4 weeks in 30 of 32 patients (94%). Grafts originated from mismatched family donors in 17 patients (55%), from matched family donors in 6 patients (19%), and from unrelated marrow or umbilical cord blood donors in 8 patients (26%). Thirteen patients received secondary or tertiary transplants. After transplantation, 21 of 31 patients were reported alive at a mean follow-up of 7.9 years (range: 0.6-23.6 years). All patients who died beyond 6 months after HSCT had persistent or recurrent agranulocytosis due to failure of donor myeloid engraftment. In the absence of conditioning, HSCT was ineffective to overcome agranulocytosis, and inclusion of myeloablative components in the conditioning regimens was required to achieve stable lymphomyeloid engraftment. In comparison with other SCID entities, considerable differences were noted regarding age at presentation, onset, and type of infectious complications, as well as the requirement of conditioning prior to HSCT. Although long-term survival is possible in the presence of mixed chimerism, high-level donor myeloid engraftment should be targeted to avoid posttransplant neutropenia.
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures


Comment in
-
HCT for SCID: one size does not fit all.Blood. 2017 May 25;129(21):2826-2827. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-04-776419. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28546225 No abstract available.
References
-
- de Vaal O, Seynhaeve V. Reticular dysgenesia. Lancet. 1959;274(7112):1123-1125. - PubMed
-
- Friedrich W, Hoenig M, Schwarz K. Reticular Dysgenesis. In: Ochs HD, Smith ECI, Puck JM, eds. Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases: A Molecular and Cellular Approach. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press; 2014:269-273.
-
- Small TN, Wall DA, Kurtzberg J, Cowan MJ, O’Reilly RJ, Friedrich W. Association of reticular dysgenesis (thymic alymphoplasia and congenital aleukocytosis) with bilateral sensorineural deafness. J Pediatr. 1999;135(3):387-389. - PubMed
-
- De Santes KB, Lai SS, Cowan MJ. Haploidentical bone marrow transplants for two patients with reticular dysgenesis. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1996;17(6):1171-1173. - PubMed
-
- Friedrich W, Goldmann SF, Ebell W, et al. Severe combined immunodeficiency: treatment by bone marrow transplantation in 15 infants using HLA-haploidentical donors. Eur J Pediatr. 1985;144(2):125-130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

